Mapping Wildlife Habitats with GIS
Environmental challenges are growing, and so is the need to protect wildlife habitats. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology is key in this effort. It helps us understand, analyze, and manage habitats better than ever before.
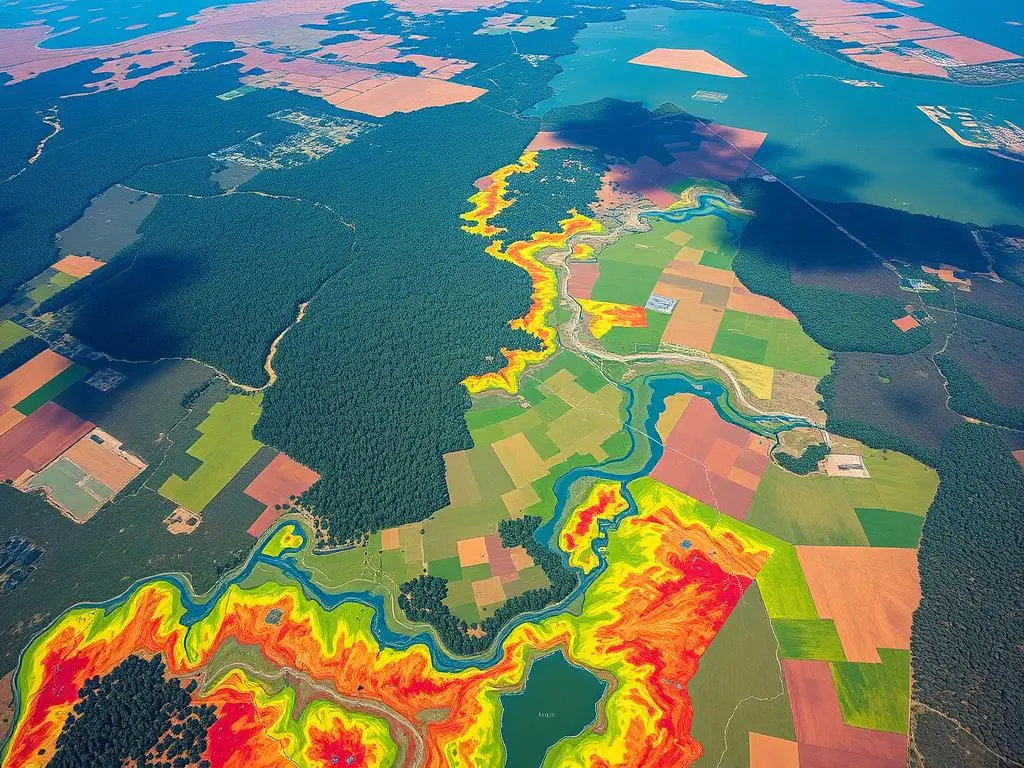
GIS is a powerful tool for mapping and monitoring wildlife habitats. It uses data from satellites, planes, and field surveys. This way, it helps us create detailed maps, track animals, and find important areas to protect.
GIS is essential for wildlife conservation. It lets us see how different parts of an ecosystem work together. This knowledge helps us make better decisions about how to use land and protect species.
GIS keeps leading the way in wildlife habitat mapping. It helps us work towards a future where wildlife habitats thrive. By using geospatial data, we can make habitats better connected and healthier.
Key Takeaways
- GIS technology has revolutionized the field of wildlife habitat mapping, enabling more precise and effective conservation efforts.
- GIS integrates spatial data from various sources to create detailed maps of habitats, track animal movements, and identify critical areas for protection.
- Spatial analysis and data visualization provided by GIS allow for a deeper understanding of the complex relationships within ecosystems, informing decision-making for land-use planning and habitat management.
- GIS remains at the forefront of wildlife habitat mapping, driving the quest for a future where thriving, interconnected habitats are the norm.
- The integration of GIS technology is crucial for biodiversity conservation and sustainable environmental management.
Understanding GIS and Its Role in Wildlife Habitat Mapping
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) have changed how we study and manage wildlife habitats. GIS is a powerful tool for handling spatial data. It’s key for environmental studies and conservation.
What is GIS?
GIS is a computer system that handles geographic information. It lets users work with maps, satellite images, and more. This technology helps us understand how different parts of the world relate to each other.
It’s especially useful for GIS mapping and wildlife habitat analysis.
Importance of GIS in Environmental Studies
In environmental studies, GIS is a must-have tool. It helps map and analyze wildlife habitats. This way, we can better understand where species live, how many there are, and how the environment affects them.
GIS-based wildlife habitat analysis finds important areas for conservation. It also tracks changes in habitats. This information is vital for planning and managing natural resources.
“GIS technology has revolutionized the way we understand and manage our natural environments. It provides unprecedented insights into the complex relationships between living organisms and their habitats, empowering us to make informed decisions for the benefit of wildlife and the planet as a whole.” – Dr. Emily Garner, Ecologist
GIS helps researchers and conservationists understand wildlife habitats better. They can see how things like plants, land shape, and human actions affect habitats. This knowledge is essential for creating effective conservation plans.
Key Components of GIS Technology
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) change how we see and manage wildlife habitats. At the heart of GIS are three main parts: Geographic Information Systems, Remote Sensing, and Spatial Analysis. Together, they offer a full way to map and protect wildlife habitats.
Geographic Information Systems
GIS is a computer system that combines hardware, software, and data. It helps researchers and conservationists work with spatial information. They can store, change, and show data about wildlife habitats. This helps them make smart choices and plan well.
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing, like satellite images and aerial photos, is key in GIS for wildlife mapping. It gathers data on habitats, like plants, water, and land shape. This info is then used in GIS for more analysis and display.
Spatial Analysis
Spatial analysis in GIS lets researchers understand habitat data better. It helps find out about habitat breaks and paths, and how species live and move. This knowledge is vital for making smart choices in wildlife protection.
By using GIS components and remote sensing for wildlife, experts can really get to know wildlife habitats. This knowledge helps them create good plans for keeping habitats safe, fixing them, and managing them well.
Types of Wildlife Habitats Mapped Using GIS
GIS technology is more than just showing data. It helps us map and study different wildlife habitats. From forests to grasslands and even cities, GIS is key to understanding and protecting these areas.
Forest Ecosystems
Forests are vital for our planet, supporting many species. GIS mapping lets us track forest health and plan for their future. It uses data from space to help conservationists.
Wetlands
Wetlands are full of life and crucial for our planet. GIS mapping helps us find and protect these areas. It’s important for keeping these habitats safe from harm.
Grasslands
Grasslands are home to many animals. GIS mapping helps us understand and care for these habitats. It guides us in protecting these natural spaces.
Urban Areas
As cities grow, so does the need to protect wildlife. GIS mapping helps find green spaces in cities. It’s key for balancing human needs and wildlife preservation.
GIS technology helps us understand and protect wildlife habitats worldwide. Through GIS ecosystem mapping, we can make better choices. This ensures the survival of our planet’s wildlife habitat types.
Benefits of GIS in Wildlife Habitat Mapping
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have changed how we map wildlife habitats. They use spatial data and analysis to help conservation and environmental management. This has brought many benefits to the field.
Enhanced Data Visualization
GIS is great at showing complex data in simple ways. It lets researchers and conservationists make detailed maps. These maps show where wildlife habitats are, how they connect, and what they look like.
This makes it easier for people to understand how different ecosystems work together. It helps find important areas to protect and manage.
Improved Accuracy of Habitat Assessments
GIS has made habitat assessments more accurate. It combines data from satellites, planes, and field work. This way, researchers can make detailed and accurate maps of habitats.
This accuracy is key for making good conservation plans. It helps see how changes in the environment affect wildlife.
Better Decision-Making
GIS gives decision-makers the insights they need. It helps find the most important areas for conservation. It also helps decide where to put resources and how to manage habitats.
This way of making decisions is based on data. It means conservation efforts are focused and effective. This helps wildlife and their habitats thrive.
GIS has been a big help in mapping wildlife habitats. It offers many benefits for keeping our ecosystems healthy. As GIS technology gets better, we can expect even more help for wildlife conservation.
Case Studies of GIS in Wildlife Habitat Mapping
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) has changed how we protect wildlife habitats. It uses spatial data and analysis to help conservationists. Let’s look at some examples of GIS in action.
Analysis of Habitat Distribution in National Parks
National parks are key for many plants and animals. GIS helps map habitats in these parks. It looks at things like plants, height, and water sources.
This info helps manage parks. It guides efforts to protect species and their homes.
Tracking Endangered Species
Keeping an eye on endangered species is crucial. GIS and GPS have made tracking easier. They help understand where species go and what they need.
This knowledge helps save species. It stops them from disappearing forever.
Habitat Restoration Projects
Fixing damaged habitats is hard work. GIS is key in planning and doing this work. It maps the area, finds what needs fixing, and makes plans.
GIS uses data from different sources. This helps restore habitats. It brings back endangered species tracking and connects ecosystems.
GIS has changed wildlife habitat mapping. It’s a big help in conservation. With GIS, experts can make better choices and protect our planet’s biodiversity.
Challenges in Using GIS for Wildlife Habitat Mapping
Geographic information systems (GIS) have changed how we map wildlife habitats. Yet, they face challenges. It’s key to know these hurdles as conservation efforts grow.
Data Availability and Quality
Getting good data is a big challenge. GIS challenges often come from bad data. This can mess up how we see habitats and make wrong choices.
Finding wildlife data quality is hard in places few people visit. It’s tough to collect data in these areas.
Technical Expertise Required
Using GIS well needs a lot of skill. People must know a lot about GIS, remote sensing, and how to analyze data. Learning this can be hard, and it costs a lot to keep a team skilled.
Environmental Changes
The environment is always changing. This makes it hard to keep GIS data up to date. Changes like climate change and human activities can change habitats fast.
Keeping GIS models current is a big job. It’s a challenge for those trying to save wildlife habitats.
| Challenge | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Availability and Quality | Incomplete or inaccurate datasets | Flawed habitat assessments and poor decision-making |
| Technical Expertise Required | Steep learning curve and high costs for GIS training and maintenance | Barriers to adoption and effective implementation of GIS in wildlife conservation |
| Environmental Changes | Rapid alterations to the landscape due to factors like climate change and human development | Outdated GIS data and models, requiring constant updates and adjustments |
GIS is still a great tool for wildlife mapping. But, we must work on data quality, skill needs, and keeping up with environmental changes. This way, we can use GIS to its fullest to protect nature.
Integrating GIS with Other Technologies
The field of wildlife habitat mapping has seen big changes with the use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and new technologies. This mix has changed how we study and protect wildlife habitats.
Drones and Aerial Surveys
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), or drones, are now key in GIS integration. They have high-resolution cameras and sensors. These drones can take detailed pictures and data for GIS software.
This lets us map hard-to-reach wildlife habitats. It gives us a full view of the landscape and where animals live.
GPS Tracking
Global Positioning System (GPS) tracking has also changed wildlife tracking technology. By putting GPS devices on animals, we can track their movements. This includes where they go, how they migrate, and what habitats they like.
This data helps us understand animal behavior and what affects their habitats. It’s then used in GIS for detailed analysis and visualization.
Machine Learning
Adding machine learning to GIS has made wildlife habitat mapping even better. These algorithms can look through lots of data, like satellite images and GPS info. They find patterns and trends that humans might miss.
This leads to better habitat assessments and finding key areas for conservation. It also helps predict how environmental changes might affect habitats.
The combination of GIS with drones, GPS, and machine learning has changed wildlife habitat mapping. It helps researchers and conservationists make better decisions and use more effective strategies.
Community Involvement in Habitat Mapping Projects
In wildlife conservation, community efforts are key. By getting local people involved in mapping habitats, we gain valuable insights. This helps ensure these projects succeed over time.
Engaging Local Communities
Local people know their ecosystems best. By working with them, habitat mapping projects get a wealth of knowledge. This knowledge comes from years of living in the area.
Through workshops and training, local residents can help collect data. This makes the data more accurate and relevant. It also builds a sense of responsibility among community members.
Citizen Science Initiatives
Citizen science has changed community-based conservation for the better. By using citizen science in GIS, projects can reach more people. This means more data and insights from volunteers.
- Mobile apps and web platforms make it easy for people to report wildlife sightings and map vegetation.
- When people help collect data, they become more connected to their environment. This encourages them to care for it.
- Community involvement improves data quality and raises awareness. It also keeps people involved in conservation for the long haul.
By working together and using citizen science, habitat mapping projects can achieve great things. Local knowledge and commitment are crucial for protecting our habitats and species.
Future Trends in GIS and Wildlife Habitat Mapping
The field of geographic information systems (GIS) is growing fast. New technologies and big data will change how we map wildlife habitats. These changes will help us protect nature better.
Advancements in Technology
New tech will make GIS better for mapping wildlife habitats. Drones and satellite images will give us more detailed views of habitats. Artificial intelligence will help us predict and track changes in the environment.
Big Data and Its Implications
Big data from many sources is changing how we map habitats. The future of GIS will be heavily influenced by the integration of big data analytics. This will help us understand habitats and species better. We can then make better choices to protect them.
| Emerging Trend | Potential Impact on Wildlife Habitat Mapping |
|---|---|
| Advancements in Sensor Technology | Improved data collection and real-time monitoring of habitat conditions |
| Integration of AI and Machine Learning | Enhanced predictive modeling and decision-making capabilities |
| Increased Availability of Big Data | Deeper insights into habitat dynamics and species-environment interactions |
As GIS and big data evolve, we’ll have better tools for conservation. We’ll understand and protect habitats better. By using new tech, GIS will keep helping us manage wildlife sustainably.
Selecting the Right GIS Software for Habitat Mapping
Choosing the right GIS software is key for wildlife habitat mapping. GIS, or Geographic Information Systems, helps collect, analyze, and show spatial data. This is crucial for understanding and protecting natural habitats.
Popular GIS Software Options
There are many GIS software options, each with its own strengths. Some top ones include:
- ArcGIS – A suite of tools for managing, analyzing, and mapping spatial data, by Esri.
- QGIS – An open-source GIS platform with advanced features for habitat mapping.
- Google Earth Engine – A cloud-based platform for analyzing big satellite and geospatial datasets.
- GRASS GIS – An open-source GIS software with strong spatial analysis capabilities.
Factors to Consider in Software Selection
When picking GIS software for your project, consider these factors:
- Project Requirements – Think about what your project needs, like data types, scale, and outputs.
- User Expertise – Match the software with your team’s GIS skills and comfort.
- Budget Constraints – Check the software’s cost, including fees, hardware needs, and training.
- Interoperability – Make sure the software works well with other tools and technologies.
- Community Support – Choose software with a big, active user community for help and resources.
By weighing these factors, you can pick the GIS software that fits your project’s needs. This will help you use geospatial technology for conservation.
Training and Resources for GIS in Wildlife Studies
Learning Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is key for wildlife conservation experts. There are many educational programs, workshops, and online resources. They help people improve their GIS skills for mapping and analyzing wildlife habitats.
Educational Programs and Workshops
Universities and conservation groups offer GIS training programs and workshops. These are designed for wildlife biologists and conservationists. They give hands-on experience with GIS software and chances to work with field experts. Some well-known options include:
- Graduate-level GIS certificate programs at universities with strong environmental science departments
- Workshops and short courses hosted by national parks, wildlife agencies, and non-profit organizations
- Intensive GIS training bootcamps or summer institutes focused on wildlife conservation and habitat mapping
Online Resources and Tutorials
For those who can’t attend in-person training, there are many online GIS resources and tutorials. Aspiring wildlife GIS practitioners can find free and low-cost ways to learn, including:
- Online courses and video tutorials on popular GIS software like ArcGIS, QGIS, and Google Earth Engine
- Webinars and virtual workshops hosted by professional organizations and industry experts
- Interactive GIS mapping and analysis projects shared through platforms like GitHub and Kaggle
- Educational blogs, forums, and discussion groups dedicated to the use of GIS in wildlife conservation
By using these varied training opportunities, individuals can get the GIS training and wildlife conservation education needed. This helps them contribute to habitat mapping and preservation efforts worldwide.
“Continuous learning and skill development are essential in the rapidly evolving field of GIS-based wildlife habitat mapping.”
Conclusion: The Future of GIS in Wildlife Conservation
GIS is a key tool in mapping wildlife habitats. It has a big role in the future of conservation. Conservationists and researchers need to use GIS to understand our planet’s ecosystems better.
Call to Action for Conservationists
Now is the time for conservationists to use GIS. It helps them make better decisions and use resources wisely. With GIS, they can protect endangered species and their homes more effectively.
The Role of GIS in Sustainable Practices
GIS is not just for conservation. It helps with sustainable wildlife management too. It shows how species and their habitats are connected. This information is crucial for planning and managing ecosystems.
GIS helps us find a balance between nature and human needs. It guides us in creating a future where wildlife and people can live together.