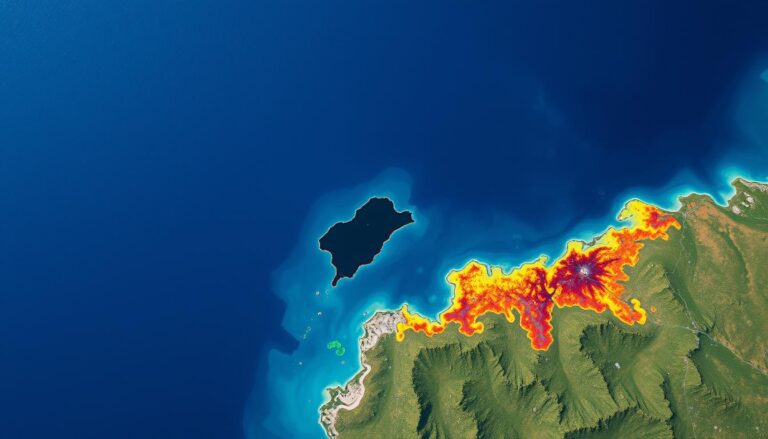
Soil Erosion Mapping with GIS
Soil erosion is a big problem that harms our land. But, new GIS technology is changing how we fight it. This article shows how GIS helps us understand and stop soil erosion. It’s a guide for experts, leaders, and those who care about the environment.
Key Takeaways
- GIS technology has transformed soil erosion mapping, enabling more accurate assessment and targeted interventions.
- Spatial analysis techniques in GIS allow for the identification of high-risk areas and the development of effective erosion control strategies.
- Integrating GIS with remote sensing and field data collection enhances the understanding of soil erosion drivers and patterns.
- Collaborative efforts involving stakeholders, local communities, and government agencies are crucial for effective soil erosion mapping and management.
- Continued advancements in GIS technology and its integration with climate change models will shape the future of sustainable land use and soil conservation.
Importance of Soil Erosion Mapping
Soil erosion is a big problem that affects land, farming, and nature. It’s key to map and understand soil erosion to fight it and use land wisely.
Understanding Soil Erosion Impacts
Soil erosion means losing topsoil, which plants need to grow. It also harms water, raises flood risks, and messes with nature. By mapping erosion, we can see where to act first.
Role of GIS in Environmental Management
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are vital for managing the environment, like soil erosion. GIS helps analyze and show data about erosion. This lets managers make better choices for land use and conservation.
| Key Impacts of Soil Erosion | Role of GIS in Addressing Soil Erosion |
|---|---|
|
|
GIS helps land managers and policymakers make better choices. This is key to keeping our natural resources healthy and productive for the future.
Key Concepts in Soil Erosion
It’s important to know about soil erosion types and what causes it. This knowledge helps us manage land better and protect it. Let’s explore the main ideas about soil erosion and its forms.
Types of Soil Erosion
Soil erosion happens in different ways, each with its own effects. The main types are:
- Water Erosion – Water moves soil away, especially with heavy rain and bad drainage.
- Wind Erosion – Wind takes soil away, mainly in dry areas with little plants.
- Tillage Erosion – Farm tools move soil down slopes over time.
- Gravity Erosion – Soil moves down slopes because of gravity, causing landslides.
Factors Contributing to Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is complex, with many causes. Both nature and human actions play a part. Key factors include:
- Climate – Weather affects how fast soil erosion happens.
- Topography – Steep slopes make soil more likely to erode.
- Soil Characteristics – Soil’s texture and organic matter help it resist erosion.
- Vegetation Cover – Plants help keep soil in place and reduce erosion.
- Land Use and Management – Bad farming and cutting down trees increase erosion.
Knowing about soil erosion types and factors is key. It helps us find ways to stop land from getting worse and manage it well.
“Soil erosion is one of the most serious environmental challenges facing humanity, with far-reaching consequences for food security, water resources, and ecosystem health.” – Dr. Jane Doe, Soil Scientist
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Basics
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are powerful tools for analyzing and visualizing data about places. They are key for mapping soil erosion. Let’s look at what GIS is made of and the different software options.
Essential GIS Components
A GIS has several important parts that work together. They help capture, manage, analyze, and show data about places. These parts include:
- Data input: Getting information from sources like satellite images, field surveys, and digital databases.
- Data management: Storing spatial data in a way that’s easy to access, often using databases or file systems.
- Data analysis: Using techniques like modeling and statistical analysis to understand the data.
- Data visualization: Showing the data as maps, charts, and graphs to help make decisions.
GIS Software Overview
There are many GIS software options, each with its own strengths. Some popular ones are:
- ArcGIS: A full set of spatial analysis tools from Esri, a top GIS provider.
- QGIS: An open-source GIS app with a big user base and lots of plugins.
- Google Earth Engine: A cloud-based platform with lots of satellite images and data for advanced GIS components and analyses.
- R and Python: Programming languages with GIS libraries like sf and geopandas for custom analysis.
These GIS software options have different features for various needs. They help with soil erosion mapping and environmental management.
Techniques for Mapping Soil Erosion
Mapping soil erosion accurately is key for protecting our environment. We’ll look at the main methods used for this, focusing on remote sensing and field surveys. These tools help us collect important data.
Remote Sensing Applications
Remote sensing is a powerful tool for soil erosion mapping. It uses satellite images and aerial photos to see the land from above. This lets experts spot areas where soil erosion is happening.
These images help find changes in plants, soil, and land shape. All these changes show where soil erosion is a problem. Thanks to new tech, remote sensing is getting better at showing soil erosion at all levels.
Field Surveys and Data Collection
Even with remote sensing, field surveys and data collection are vital. They give us real data from the ground. This data helps check the accuracy of remote sensing and gives us a closer look at the local issues causing erosion.
- Field surveys give us detailed data to improve remote sensing models.
- They help us understand soil texture, slope, and plant cover, which are key for predicting erosion.
- Combining field data with remote sensing gives us a full picture of soil erosion.
Using both remote sensing and field surveys, we can make detailed and accurate soil erosion maps. These maps are essential for good soil conservation and management.
Modeling Soil Erosion with GIS
Understanding soil erosion is key for good environmental management. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are a powerful tool for modeling and predicting soil erosion. This section looks at how erosion prediction models and spatial analysis in GIS mapping work.
Erosion Prediction Models
Soil erosion prediction models use algorithms and equations to estimate soil loss. They consider rainfall, slope, soil type, and land cover. GIS software helps apply these models with its spatial data and analysis tools.
- Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE): A widely used model that calculates the potential soil loss based on factors like rainfall, soil erodibility, slope length, and vegetation cover.
- Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE): An advanced version of USLE that incorporates additional parameters for more accurate erosion predictions.
- Erosion Potential Model (EPM): A model developed for specific regions, taking into account local climate, soil, and land use characteristics.
Using Spatial Analysis for Predictions
GIS mapping and spatial analysis are key for visualizing and predicting soil erosion. By combining data layers like elevation, soil properties, and land use, GIS creates detailed erosion prediction models. These models help spot high-risk areas and guide soil conservation efforts.
GIS-based erosion modeling offers insights for decision-makers. It helps them make choices for sustainable land management and environmental protection.
Data Sources for Soil Erosion Mapping
Getting accurate data is key for good soil erosion mapping. Experts use many sources to make detailed erosion reports. Satellite imagery and soil and water conservation data are especially important.
Satellite Imagery
Satellite tech has changed how we get and use data for soil erosion mapping. High-resolution satellite imagery shows us land cover, topography, and more. This info helps make accurate erosion models and spot risky areas.
Soil and Water Conservation Data
Conservation data from government and non-profits is also vital. It includes soil types, rainfall, and land use. This helps find erosion causes and find solutions.
| Data Source | Key Information | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Satellite Imagery | Land cover, topography, vegetation, and other environmental factors | Provides detailed, up-to-date information on a large scale |
| Soil and Water Conservation Data | Soil types, rainfall patterns, land management practices | Helps identify the underlying causes of erosion and develop tailored solutions |
Using these GIS data sources helps experts and policymakers understand soil erosion well. They can then use this knowledge to protect our soil.

Case Studies in Soil Erosion Mapping
Soil erosion mapping is key for protecting our environment. Many erosion mapping projects have been done around the world. They show how Geographic Information Systems (GIS) can help fight soil loss.
Successful Mapping Projects
In China’s Loess Plateau, a big case study was done. Researchers used remote sensing and GIS to map soil erosion. Their work helped plan better land use and early warning systems.
In India’s Himalayas, GIS applications were used to map erosion risks. They combined satellite images and soil data. This helped policymakers focus on where to save the most land.
Lessons Learned from Past Efforts
These erosion mapping projects were mostly successful. But they taught us important lessons. It’s crucial to include local knowledge, improve data quality, and work together to keep these efforts going.
Also, using GIS applications with climate models is key. It helps us understand soil erosion better and its effects on our environment.
“Soil erosion mapping has proven to be a powerful tool in guiding sustainable land management practices and informing policymakers on the critical issues facing our environment.”
Challenges in Soil Erosion Assessment
Soil erosion mapping is a complex task. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have helped a lot. But, there are still big data quality and technical limitations to tackle.
Data Quality Issues
Getting good data on soil erosion is hard. It’s tough to find reliable data on soil type, topography, and land use, especially in remote areas. Different ways of collecting data and varying resolutions can also make models less accurate.
Technical Challenges
Soil erosion is complex to model. It involves many factors like rainfall, vegetation, and soil characteristics. Advanced computers and smart algorithms are needed to understand these interactions.
Researchers are trying to solve these technical challenges and improve data quality. New tools like remote sensing, machine learning, and spatial analysis are helping. These advancements make erosion mapping more accurate and detailed.
By tackling these challenges, we can better understand soil erosion. This knowledge is key for sustainable land use, environmental protection, and fighting climate change. More research and innovation are needed to move forward in this important field.
Stakeholder Engagement in Erosion Mapping
Soil erosion mapping projects succeed when they involve key stakeholders. This includes local communities and government agencies. Collaboration and diverse perspectives make these efforts more effective and impactful.
Involving Local Communities
Local communities know a lot about their land and erosion challenges. Their input is crucial for understanding and solving erosion problems. Strategies for engaging them include:
- Holding public workshops and town hall meetings to gather input and feedback
- Recruiting and training local residents as citizen scientists to assist with data collection
- Developing educational programs to increase awareness and foster a sense of stewardship
Collaboration with Government Agencies
Government agencies have valuable data and resources. They can enhance soil erosion mapping efforts. Successful partnerships include:
- Partnering with the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) to access high-resolution satellite imagery and terrain data
- Collaborating with the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) to integrate soil and water conservation data
- Engaging with local planning departments to incorporate erosion mapping into land use and development strategies
By focusing on community engagement and government collaboration, soil erosion mapping projects become more effective. They address the complex challenges of this critical environmental issue.
Future Trends in Soil Erosion Mapping
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) is getting better, opening new doors in soil erosion mapping. These updates will make erosion predictions more accurate. They will also work well with the latest climate change models, giving us a deeper look into this big environmental problem.
Advances in GIS Technology
GIS tech is growing fast, making soil erosion mapping better. New tools in remote sensing, spatial analysis, and data handling are helping us see erosion more clearly. With more powerful computers and high-resolution satellite images, we’re changing how we map soil erosion.
Integration with Climate Change Models
Climate change is making soil erosion more urgent. Soon, we’ll link soil erosion mapping with advanced climate models. This will help us predict erosion risks better and find ways to stop it. Combining GIS and climate science is key to tackling soil erosion as the climate changes.
New trends in soil erosion mapping are exciting. They come from better GIS tech and working with climate models. These steps will help us understand soil erosion better. They will guide us in making decisions and finding ways to fight soil erosion, keeping our landscapes safe for the future.
| Technological Advancement | Benefit for Soil Erosion Mapping |
|---|---|
| High-resolution satellite imagery | Improved identification and monitoring of erosion patterns |
| Advanced spatial analysis tools | Enhanced modeling and prediction of erosion risks |
| Increased computational power | Ability to process large datasets and run complex simulations |
| Integration with climate change models | Comprehensive understanding of the impacts of climate variability on soil erosion |
Best Practices for Soil Erosion Mapping
Effective soil erosion mapping needs a detailed and organized method. Here are some key steps and why ongoing monitoring is vital for accurate results.
Methodological Recommendations
For soil erosion mapping, experts suggest several methods:
- Use remote sensing data like satellite images and aerial photos to understand the area well.
- Do field surveys and data collection to check the remote sensing info and make sure erosion assessments are right.
- Use a multi-scale approach to see both big and small erosion patterns and processes.
- Apply strong spatial analysis, like GIS modeling, to measure erosion extent and severity.
- Work with local groups, like government and community members, to add their insights to the mapping.
Importance of Continuous Monitoring
Soil erosion changes over time due to many factors. Keeping an eye on it is key to track changes and make smart decisions.
Regularly updating soil erosion maps and watching how mitigation efforts work helps in many ways:
- Spot new problem areas and focus on saving them.
- See if soil erosion control plans are working and tweak them if needed.
- Study how land use and climate changes affect erosion patterns.
- Give policymakers and stakeholders the data they need for sustainable land use plans.
Following these best practices and keeping up with monitoring ensures soil erosion mapping is effective. It supports environmental protection and sustainable land use.
Conclusion: The Future of Soil Erosion Mapping with GIS
Soil erosion mapping with GIS is key to protecting our soil. It helps us understand erosion causes, predict it, and fight it. GIS is a crucial tool for managing soil.
Summary of Key Findings
This article shows how vital soil erosion mapping is. It talks about GIS’s role in managing the environment and improving data collection. The examples given show how GIS helps communities and guides policy makers.
Call to Action for Researchers and Practitioners
Looking ahead, GIS will keep getting better for soil erosion mapping. We need researchers and practitioners to keep up with new tech. By working together and listening to local needs, we can make sure our soil is safe for the future.