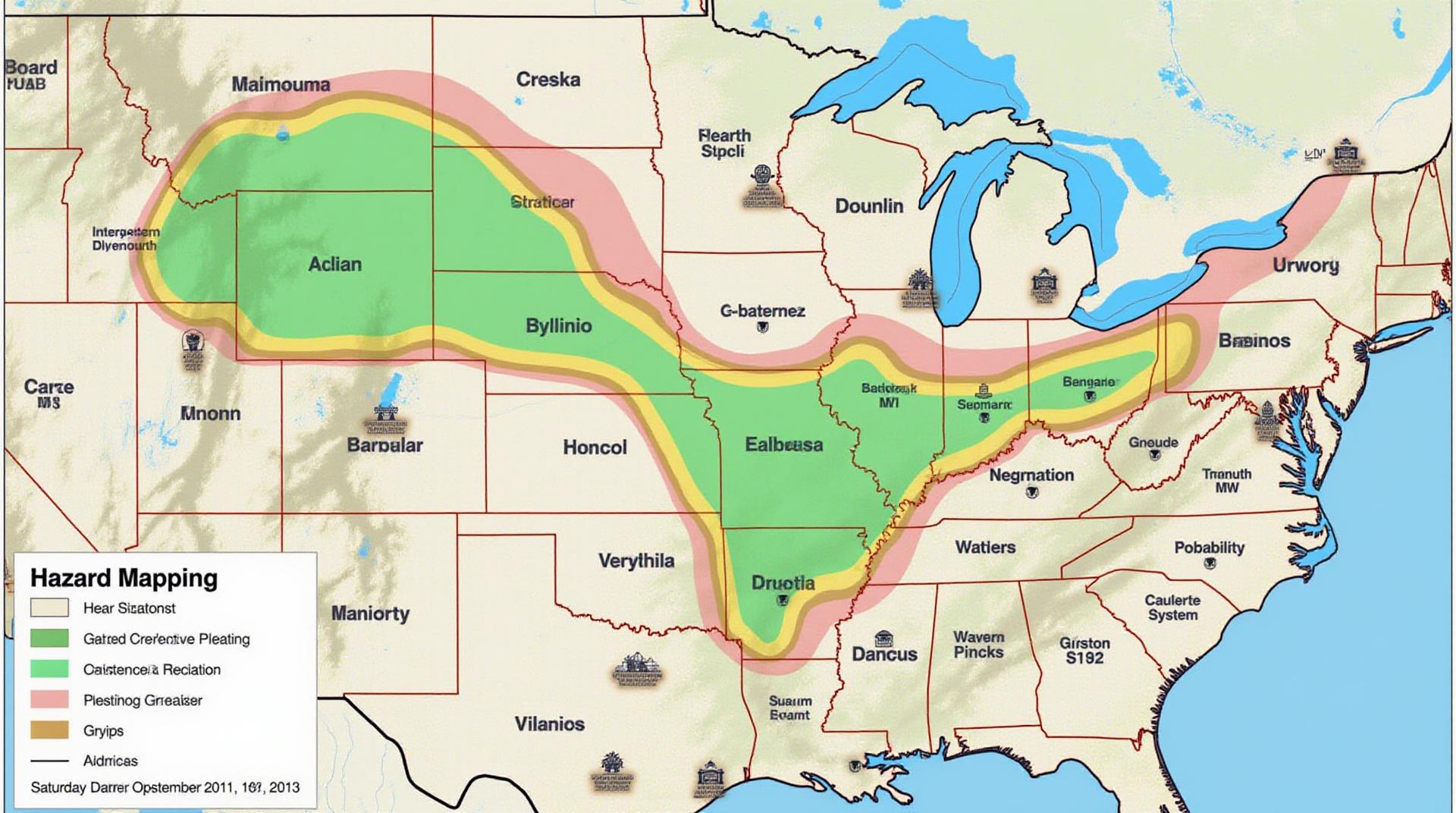
AI and GeoSpatial Data for Risk Management – Hazard Mapping
## AI and GeoSpatial Data for Risk Management – Hazard Mapping: A Powerful Combination
As our world becomes increasingly interconnected and our societies more reliant on complex infrastructure, the need for robust risk management strategies becomes more imperative. In this context, **GeoAI**, a powerful fusion of geographic information systems (GIS) and artificial intelligence (AI), stands as a revolutionary tool with significant promise in mitigating hazards and promoting informed decision-making.
What is GeoAI?
GeoAI refers to the application of AI algorithms and techniques specifically designed to analyze and interpret geo-spatial data. Think of it as unleashing the intelligence of machines to reveal patterns, predict future outcomes, and provide insights hidden within vast mountains of geographically-referenced data.
### Key Features of GeoAI for Hazard Mapping
The key differentiators of geoAI for hazard mapping include:
* **Data Integration:** GeoAI systems rapidly ingest and process planetary, satellite, and terrestrial data from various sources. This includes imagery, remote sensing data, weather patterns, geological features, and more, creating a holistic picture of a region or location.
* **Advanced Analytics:** GeoAI leverages machine learning algorithms and predictive modeling, allowing for the identification of patterns and trends that would be impossible to detect through human analysis alone. This includes the ability to analyze thousands of data points simultaneously to find even subtle correlations, leading to more accurate hazard predictions.
* **Real-time Observations:** GeoAI’s solution extends beyond static data analysis. It incorporates real-time data, such as crowdsourced information or official updates, for up-to-date hazard mapping, promoting dynamic risk awareness.
### Benefits of GeoAI for Risk Management
Integrating GeoAI into risk management offers numerous advantages:
* **Enhanced Forecast Accuracy:** GeoAI models are constantly evolving, learning to interpret historical data, and extracting correlations between factors to provide significantly more accurate hazard predictions.
* **Site Characterisation:** Analysis of past events and geological data allows GeoAI to provide details on the ground, including soil composition and ground conditions that can significantly impact hazard events.
* **Targeted Disaster Response:** Incorporating real-time information and location data, GeoAI can help coordinate disaster response efforts towards the most vulnerable areas.
* **Improved Decision Making:** By providing granular insight and actionable intelligence, GeoAI empowers decision-makers in city planning, infrastructure management, and other fields to make informed choices at every juncture.
### Practical Applications of GeoAI in Hazard Mapping
* **Earthquake Risk Assessment:** GeoAI has been instrumental in identifying fault lines, predicting earthquake magnitudes, and identifying vulnerable zones – empowering planners and policymakers with critical insights for structural design and emergency plans.
* **Flood Zone Mapping:** By analysing tide tables, rainfall data, and topographical information, GeoAI models can calculate flood risk zones and optimize flood prevention strategies.
* **Wildfire Mitigation:** The information analyzed by AI technologies allows for efficient ignition spot identification and terrain prediction, leading to more proactive arson prevention and wildfire management efforts.
* **Transportation Network Resilience:** Urban traffic flow analysis, congestion mapping, and road infrastructure vulnerability assessment can all be significantly impacted by AI-based routing, predictive modeling, and building management.
### Resources to Get Started
* **AI-powered Platforms:** Companies such as Google Earth Engine, QGIS, and ArcGIS offer comprehensive platforms designed for handling complex geospatial data, incorporating AI for predictive analysis and hazard mapping.
* **Open-source Datasets:** Resources like the GlobalOpen Data Initiative (GO-DATA) and the GeoNode web portal provide access to vast geospatial datasets readily available for any use case.
* **Online Courses and Tutorials:** Platforms like Coursera and DataCamp offer numerous free and paid courses on GeoAI and its applications.
### Conclusion
GeoAI is not just a new technology, but a paradigm shift. This revolution promises to unlock new levels of predictability and intelligence within the world of risk management and actively empowers individuals and communities to proactively prepare for future events, mitigating risks and shaping a safer future.
## Frequently Asked Questions – AI-Geospatial Data Risk Management – Hazard Mapping
This guide addresses common questions about AI-geospatial-data-risk-management-hazard-mapping.
### What is AI-geospatial data risk management-hazard mapping?
AI-geospatial data risk management – hazard mapping utilizes artificial intelligence and geospatial information to identify and assess risks associated with geographic areas. It can help to predict and mitigate potential damage from events such as natural disasters, infrastructure failures, and others.
### What formats are provided?
* **Data Formats:** We offer the ability to work with a variety of data formats, including GeoJSON, KML, Shapefiles, and more.
https://github.com/Miaar/Geojson
### What are the benefits of AI-geospatial data risk management – hazard mapping?
This method offers practical advantages, including:
* **Improved Accuracy & Efficiency:** Utilizing AI and geospatial analysis provides enhanced data accuracy compared to traditional methods, significantly improving overall efficiency and reducing data bias.
* **Dynamic Adaptations:** AI can effectively adapt to dynamic changes in geographically influenced risks, allowing for more accurate and continuous threat assessments.
* **Early Warnings & Safety Measures:** Based on the predicted risk maps, AI can generate early warnings, enabling early action and potentially saving lives or minimizing damage before events reach critical levels.
### What is my data needed for?
* Accessing your own data is the initial step. This ensures accurate risk assessments.
* Prepare a diverse geological dataset that accounts for the locations and specific risks you wish to analyze. This might be data from sensors, satellites, and traditional geographic databases.
### How can I access tools for AI-geospatial data risk management – hazard mapping?
https://www.esri.com/en-us/software/arcgis/
### Where can I learn more about this topic?
We also recommend the following resources for learning more about the field:
* https://www.esri.com/en-us/industries/government/events/spotlight-on-hazard-mapping
* https://www.nationalnoaa.gov/
**Conclusion:**
AI-geospatial data risk management – hazard mapping is poised to be a crucial tool in the growing cycle of environmental change, disaster prediction, and risk mitigation . By leveraging AI and technology, we can manage geographic risks more effectively and create a safer future.
Actionable insights:
* Consider applying AI risk mapping technology to your organization or project, regardless of your industry.
* To estimate any potential risks, start with potential data to predict the context of geographic risk.
* Invest in training and exploring AI tools for enhanced capability and dynamic adjustments.
Let’s work together to utilize AI for a more informed and safer future.