Battle of the GNSS Surveying Rovers: E1 RTK vs. SMA20RTK vs. SMA26 – Which One Should You Choose?

Surveying professionals demand precision, durability, and efficiency from their GNSS Surveying equipment. Three standout models—E1 RTK, SMA20RTK, and SMA26—offer powerful RTK/PPK capabilities, IMU tilt compensation, and NOAA certification. But which one is the best fit for your needs?
In the realm of GNSS Surveying, the choice of equipment can significantly influence the accuracy and efficiency of the project outcomes. A thorough understanding of the features and specifications of different GNSS rovers is essential for making an informed decision. As we delve deeper into the comparison of the E1 RTK, SMA20RTK, and SMA26 models, we will also explore real-world applications and user experiences that highlight their capabilities in various surveying scenarios.
This article will not only provide technical specifications but also discuss the contexts in which each GNSS Surveying rover excels, backed by case studies from professionals who have employed these devices in the field. Understanding the nuances of GNSS technology can vastly improve the quality of your surveying work, so let’s get started.
In this in-depth comparison, we’ll break down their key features, accuracy, range, and usability to help you decide.
When considering GNSS Surveying rovers, it’s imperative to reflect on the project requirements: scale, terrain, and precision needed. Each model has its unique advantages, making it essential to align the choice with the intended use case. Let’s explore each model’s overall capability and how they compare in real-world applications.
The following table provides an overview of the key features, but we will also discuss the implications of these specifications on actual GNSS Surveying tasks.
For instance, in challenging terrains where accuracy is paramount, the differences in tilt compensation for GNSS Surveying are crucial. Let’s delve into how these features perform under various conditions.
Real-world accuracy in GNSS surveying is often influenced by environmental factors. For example, obstructions such as tall buildings or trees can affect signal quality, which in turn impacts the performance of RTK systems. Users have reported that the E1 RTK, while offering solid accuracy, struggled with multi-path issues in urban environments. On the other hand, the SMA20RTK, with its extended range, has proven advantageous in open field scenarios.
1. Overview of the Three GNSS Rovers
The stability of signal reception is another critical factor. In a construction site example involving the SMA26, users noted a significant reduction in setup time due to its superior signal processing. This translates into increased productivity, particularly on large-scale projects where time is money.
Moreover, SMA26’s half centimetre accuracy has enabled precise plotting for engineering applications where even the smallest deviation can result in costly errors. This high level of precision ensures compliance with stringent industry standards, making it an invaluable asset for surveyors working on sensitive projects.
Connectivity is another aspect that affects user experience. The SMA20RTK’s extended PPK range has made it a preferred choice for surveyors working in remote locations. For example, a recent project involving land development required extensive surveying across a 50-acre site, and the SMA20RTK delivered consistent performance without the need for a base station, thus providing flexibility and efficiency.
| Feature | E1 RTK GNSS | SMA20RTK | SMA26 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (RTK) | 1 cm | 1 cm | 0.5 cm |
| PPK Range | 5 km (UHF) | 25 km | 10 km |
| Channels | 1408 | 1408 | 1408 |
| IMU Tilt Compensation | 60° | Yes (Angle not specified) | Yes (Angle not specified) |
| Battery Life | 20 hours | Not specified | Not specified |
| Storage | Not specified | Not specified | 32GB |
| NOAA Certified | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Surveyors reported that the 5 km limitation of the E1 RTK was a constraint in larger projects, which necessitated additional equipment to achieve the desired coverage. This highlights the importance of considering the operational range of each GNSS rover during planning stages.
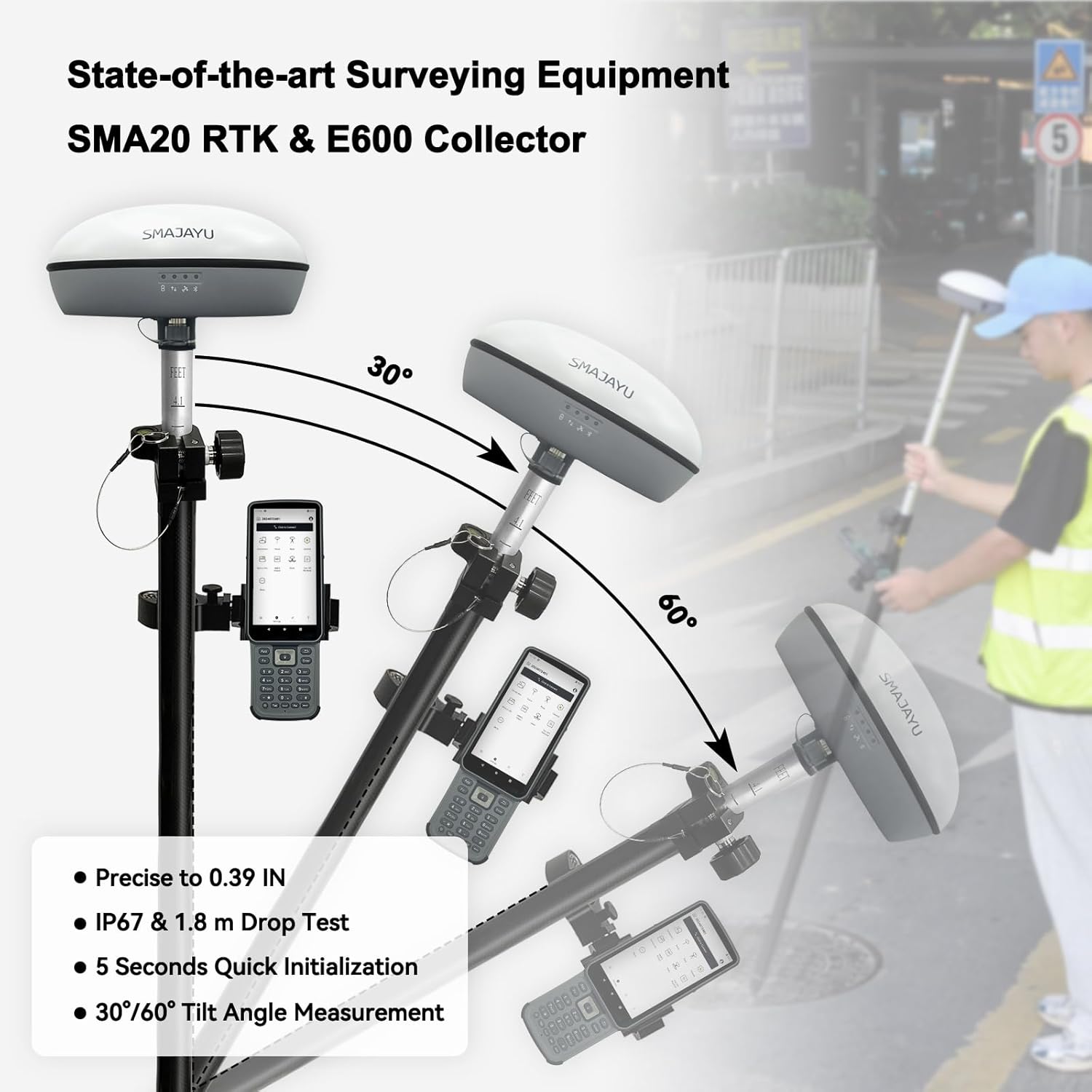
SMA20RTK PPK PPP IMU NOAA certificated GNSS RTK Rover Base Collector, Survey Software, PPK Calculation, Upto 25km by PPK, 1cm RTK Accuracy,1408channels,Static RTK Base Dual Mode(Exclude Tripod&Pole)
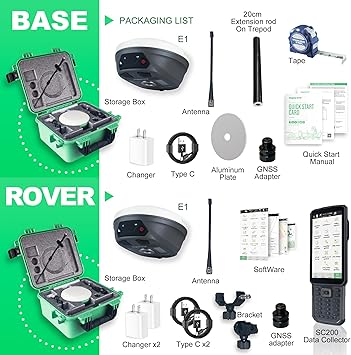
E1 RTK GNSS Survey Equipment 20 Hours Endurance RTK GNSS GPS with IMU Rover & Base Handheld Collector with Survey Software RTK Surveying Equipment,1408 Channels, 5km UHF Range,60° Tilt Survey
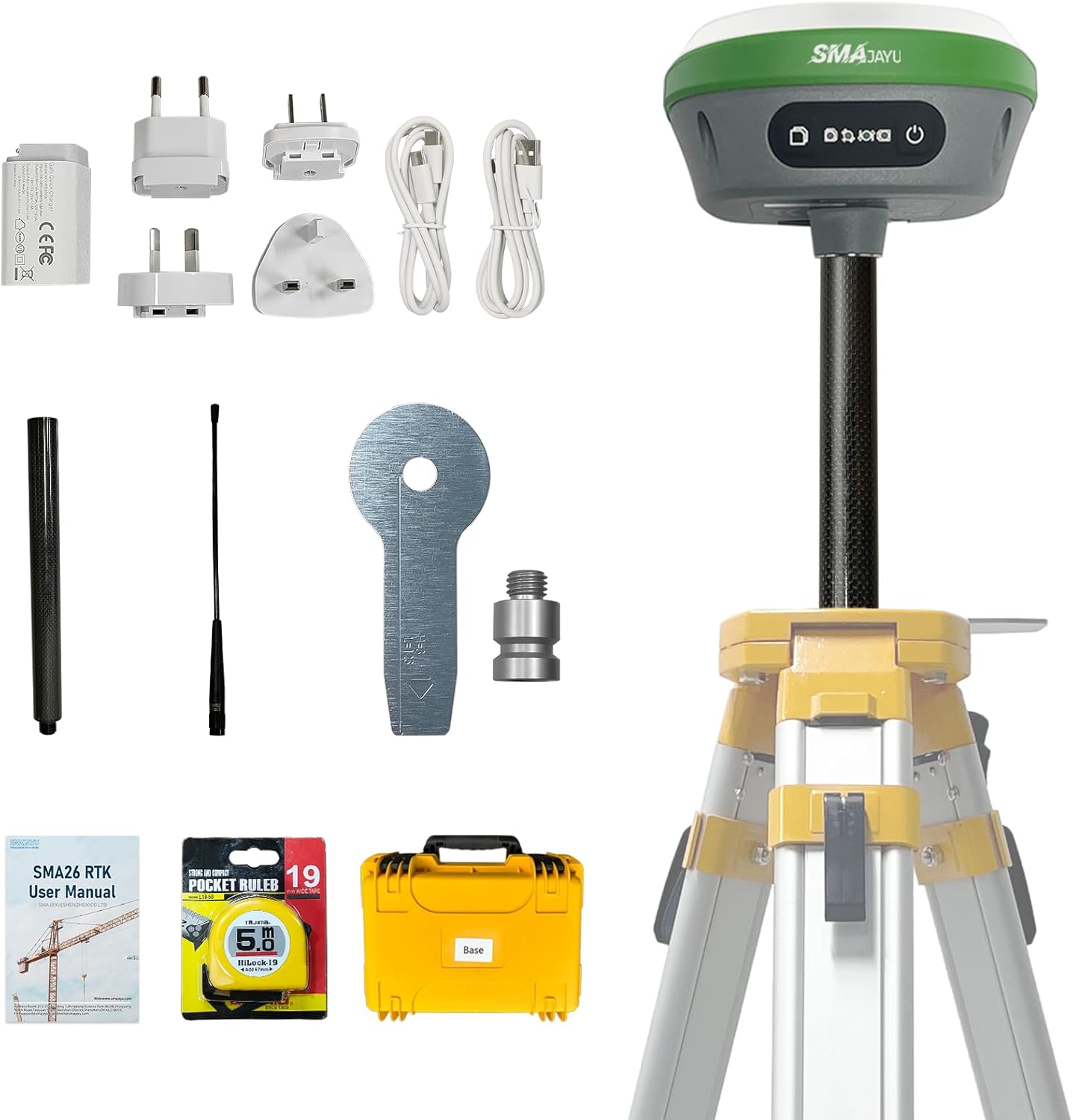

SMA26 RTK Base Station IMU High Accuracy GNSS Receiver Static Surveying NOAA certificated 32G Storage (Exclude Tripod)
2. Detailed Comparison
🔹 Accuracy & Performance
- E1 RTK & SMA20RTK: Both offer 1 cm RTK accuracy, suitable for most surveying tasks.
- SMA26: The clear winner with 0.5 cm RTK accuracy, making it ideal for ultra-high-precision work like engineering and cadastral surveys.
Tilt compensation features also play a significant role in various terrains. The E1 RTK’s capability to maintain performance at up to 60° tilt allows surveyors to operate in rugged landscapes where traditional equipment may fail. This aspect not only enhances operational versatility but also ensures accurate data collection in challenging conditions.
However, while the SMA20RTK and SMA26 do not specify their tilt angles, user experiences suggest that both models provide impressive stability, even in steep terrains. This can be a decisive factor for surveyors working in hilly regions where equipment reliability is tested.
🔹 Range & Connectivity
- E1 RTK: Limited to 5 km UHF range, best for small to medium projects.
- SMA20RTK: Dominates with 25 km PPK range, perfect for large-scale surveys without needing a base station nearby.
- SMA26: 10 km range, a middle ground between the other two.
Battery life is another critical concern, particularly for surveyors engaged in lengthy outdoor projects. The E1 RTK’s 20-hour battery life enables it to perform through an entire day of surveying without interruption. In contrast, while the SMA20RTK’s battery life remains unspecified, its PPK efficiency allows for less frequent recharges, which can be advantageous in the field.
GIS Experttgeoc2g@gmail.comEdit Profile
Data storage capabilities also influence the efficiency of surveying tasks. The SMA26’s 32GB storage allows for extensive data collection, which is crucial during comprehensive surveys involving numerous data points. In practice, this means less time spent managing data and more time focusing on fieldwork.
In contrast, while the SMA20RTK is efficient in data handling, the lack of specified battery life and storage could pose limitations for some users. Therefore, understanding how each model performs under varying conditions is essential.
The software accompanying these devices is equally important. Users have noted that all three rovers come with intuitive survey software, which simplifies the data collection process. Training sessions offered by manufacturers can further enhance users’ proficiency with these tools, ensuring they can maximise efficiency in the field.
🔹 IMU Tilt Compensation
- E1 RTK: 60° tilt compensation—great for difficult terrain.
- SMA20RTK & SMA26: Both support tilt compensation, but exact angles aren’t specified.
🔹 Battery & Storage
Compliance with NOAA certification across all models reinforces their reliability, making them suitable for professional surveying tasks where precision and dependability are paramount. Surveyors can confidently utilise these devices knowing they meet industry standards.
Ultimately, selecting the right GNSS rover is not merely about technical specifications but also about understanding how those specs translate into practical benefits for your specific surveying needs.
- E1 RTK: 20-hour endurance, excellent for long fieldwork days.
- SMA26: 32GB storage, allowing for extensive data collection.
- SMA20RTK: Battery life not specified, but PPK efficiency reduces reliance on constant RTK corrections.
For budget-conscious surveyors or those just starting, the E1 RTK provides an excellent entry point, combining essential features with affordability. Users have shared positive experiences regarding its ease of use, making it ideal for general surveying tasks.
🔹 Software & Certification
- All three come with survey software and are NOAA certified, ensuring reliability for professional use.
On the other hand, the SMA20RTK stands out for projects requiring extensive coverage without the constraints of a base station. This flexibility is invaluable in sectors like construction and mining, where surveying areas can often be spread out.
3. Which One Should You Buy?
✅ Best for Budget & General Surveying: E1 RTK
- Pros: Strong tilt compensation, good battery life, solid accuracy.
- Cons: Limited range (5 km).
- Ideal for: Small to medium projects where cost is a concern.
Lastly, for professionals in high-stakes fields necessitating the utmost precision, the SMA26 is the go-to choice. Its state-of-the-art accuracy can make a significant difference in engineering and cadastral surveys, where even the slightest error can lead to complications or financial loss.
✅ Best for Large-Scale Surveys: SMA20RTK
- Pros: Massive 25 km PPK range, NOAA certified, strong RTK performance.
- Cons: Higher price, no specified battery life.
- Ideal for: Mining, large construction sites, and long-distance surveys.
✅ Best for Ultra-Precision Work: SMA26
- Pros: 0.5 cm accuracy, 32GB storage, NOAA certified.
- Cons: Most expensive, 10 km range (less than SMA20RTK).
- Ideal for: Engineering, cadastral surveys, and high-stakes projects.
4. Final Verdict
- Need affordability & decent performance? → E1 RTK
- Working on massive sites? → SMA20RTK
- Demand the highest precision? → SMA26
Each of these GNSS rovers excels in different scenarios. Your choice depends on budget, project scale, and required accuracy.
In conclusion, understanding your specific needs—whether it’s budget constraints, project scale, or accuracy requirements—will lead to a more informed decision in selecting the right GNSS rover. Each model has unique strengths that can cater to various surveying demands.
Which one fits your surveying needs? Let us know in the comments!
Table of Contents
Take the time to evaluate your options and consult with professionals in the field to gain insights that can aid your selection process. Your choice will impact not only the success of your current project but also future endeavours in the ever-evolving landscape of surveying technology.
What has been your experience with GNSS surveying equipment? Which model do you prefer for your projects? Share your thoughts in the comments, as your insights could benefit others in the surveying community.






5 Comments