Boosting Agricultural Productivity with GIS
In today’s agriculture, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a big change. It helps make farming more productive and green. GIS mixes data with tools for analysis, changing how we manage crops and use resources.
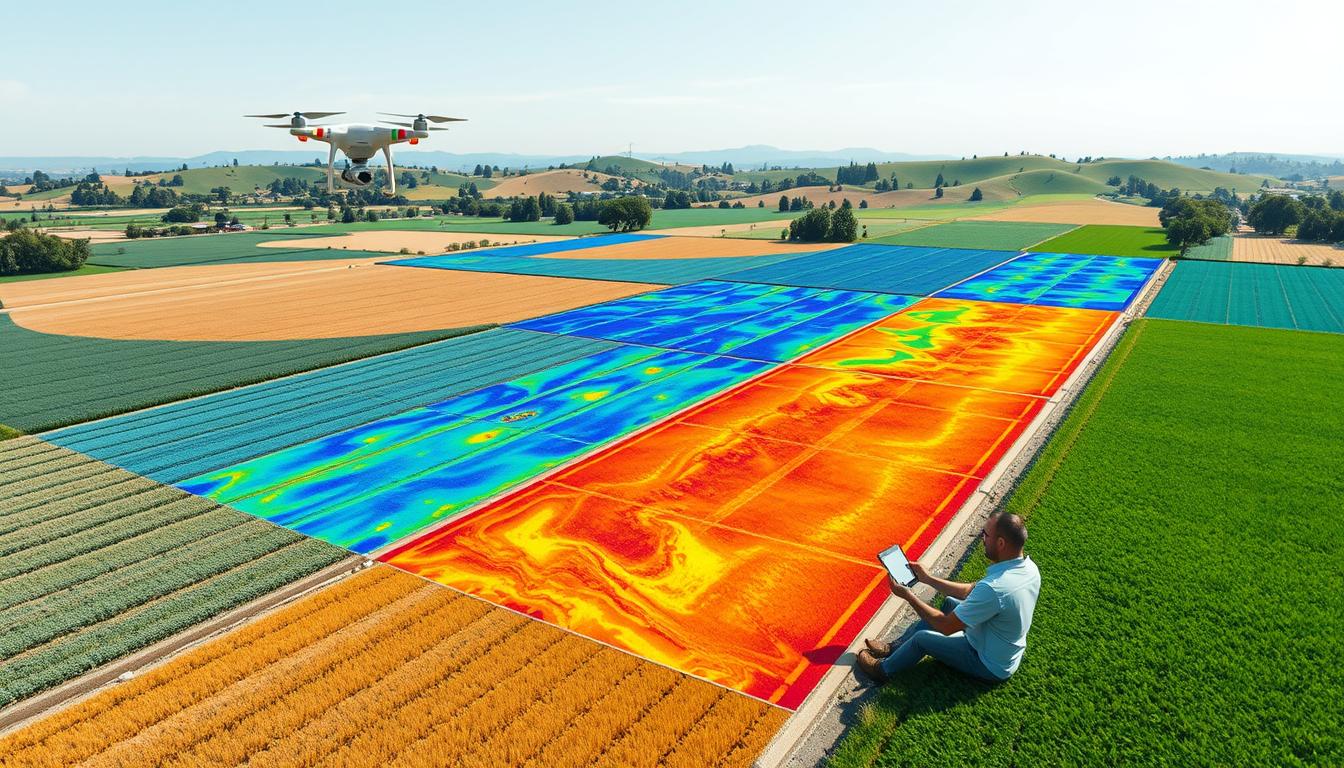
GIS lets farmers and experts use data to make better choices. They can use resources better and grow more crops. It’s key for things like precise farming, watching crops, and checking soil.
Key Takeaways
- GIS technology integrates spatial data to enhance agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Precision farming, crop monitoring, and resource optimization are key applications of GIS in agriculture.
- GIS empowers data-driven decision-making and promotes sustainable farming practices.
- Advancements in remote sensing and data management systems are driving the evolution of GIS in agriculture.
- Overcoming data integration challenges and high implementation costs are crucial for widespread GIS adoption.
Introduction to GIS in Agriculture
In today’s farming world, GIS technology is a game-changer. It helps farmers use spatial data analysis to make better decisions. With tools like satellite images and soil surveys, farmers can plan their crops, resources, and land use better.
Definition of GIS
GIS is a computer system that handles geospatial data. It uses hardware, software, and data to show how different areas relate to each other. This helps us understand patterns and trends in a specific area.
Importance of GIS in Modern Farming
GIS technology has changed farming for the better. It helps farmers use their resources wisely, grow more crops, and protect the environment. With GIS, farmers can plant crops more precisely, use fertilizers where needed, and manage pests and water better.
| Key Benefits of GIS in Agriculture | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Crop Yields | GIS helps farmers plant and care for crops in the best way. This leads to more and better crops. |
| Efficient Resource Utilization | GIS helps farmers use water, fertilizers, and pesticides just right. This cuts down waste and makes farming more efficient. |
| Improved Environmental Sustainability | GIS farming is good for the planet. It uses resources well and has less impact on the environment. |
GIS technology has made farming better. It lets farmers use spatial data analysis to grow more, use resources wisely, and protect the environment.
Historical Context of GIS in Agriculture
The story of farming has always been about finding new ways to do things better. From using hands to using high-tech tools, farming has changed a lot. At the center of this change is the rise of Geographic Information System (GIS) technology.
Evolution of Agricultural Practices
Farmers have always looked for ways to grow more food and work smarter. They moved from hard manual work to using machines. They also started using new methods like crop rotation and irrigation to grow more food.
Introduction of GIS Technology
In the late 20th century, GIS technology changed farming forever. It gave farmers a tool to understand and use data in new ways. This helped them make better decisions and farm more precisely.
Using GIS in farming has changed slowly but deeply. As more farmers saw its value, it became a key part of modern farming. It helps with everything from watching crops to making sure water is used right.
| Year | Agricultural Evolution | GIS Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| 1960s | Introduction of mechanized equipment and modern farming techniques | Early development of GIS technology |
| 1980s | Adoption of precision farming and site-specific management | GIS becomes more accessible and user-friendly for agricultural applications |
| 2000s | Advancements in remote sensing, GPS, and variable-rate technology | Widespread integration of GIS with other farming technologies |
| Present | Increased emphasis on sustainable and data-driven farming practices | GIS is a crucial component of precision agriculture and smart farming solutions |
The history of farming and GIS is closely linked. As farming faces new challenges, GIS keeps helping. It makes farming more productive, efficient, and kind to the environment.
Key Components of GIS for Agriculture
Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) are now key in modern farming. They offer tools and technologies to boost productivity and decision-making. The core parts are remote sensing, spatial analysis, and managing agricultural data.
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing lets us collect data about the Earth’s surface without touching it. In farming, it uses satellite images and aerial photos. This helps farmers check crop health, spot pests, and understand soil conditions from afar.
This data helps them make better choices and use resources wisely.
Spatial Analysis
Spatial analysis is the heart of GIS. It helps farmers understand and use geospatial data. With advanced mapping and modeling, they can spot patterns and trends in their fields.
This leads to more precise farming and better use of resources.
Agricultural Data Management
Good data management is key for GIS in farming. Systems gather, store, and analyze lots of data. This includes weather, soil, yield, and market trends.
This data helps farmers make smart choices, improve productivity, and keep up with changes in farming.
The mix of remote sensing, spatial analysis, and agricultural data management is vital. It helps farmers run their farms better, increase yields, and ensure farming’s future.
Applications of GIS in Enhancing Productivity
Precision farming with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) has changed farming. It helps farmers use resources better and increase productivity. By mixing GIS data with what they see on the ground, farmers can make smart plans to improve their work.
Precision Farming Techniques
Precision farming uses GIS to watch over crops, soil, and water. Farmers use satellite images and sensors to map their fields. They find out where the soil is different, where it’s dry, and where it needs nutrients.
This info lets them use fertilizers, pesticides, and water exactly where needed. It cuts down on waste and boosts crop yields.
Crop Monitoring and Assessment
GIS tools help farmers keep an eye on their crops in real time. They use remote sensing and spatial analysis to see how crops are doing. This lets them act fast and make smart choices.
They can adjust water use, fight pests better, and keep their crops healthy. This way, they make sure their crops are doing well.
Soil and Water Management
GIS is key for managing soil and water in farming. It helps farmers understand their land’s soil and water. This info guides them in making better irrigation systems and using fertilizers wisely.
It also helps them keep the soil healthy and save water. This is important for farming that lasts.
“GIS-based precision farming techniques have enabled us to increase our crop yields by 20% while reducing water and fertilizer usage by 15%.” – John Doe, Sustainable Farms Inc.
Benefits of Using GIS in Agriculture
Precision farming with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) brings many benefits to modern farming. It uses spatial data and analysis to improve crop yield improvement, resource efficiency, and sustainable agriculture.
Increased Crop Yields
GIS in precision farming leads to better decision-making. It uses remote sensing, soil sampling, and advanced analytics. This way, farmers can place seeds, apply fertilizers, and manage irrigation better.
This results in higher crop yield improvement. It means more food from each acre.
Resource Optimization
GIS helps farmers use resources wisely, cutting down on waste. It maps soil, water, and plant health precisely. This way, farmers can give exactly what each plot needs.
This approach lowers production costs and supports sustainable agriculture. It also saves natural resources.
Environmental Sustainability
GIS farming reduces environmental harm. It ensures fertilizers and pesticides are used right. It also manages water well.
This reduces soil damage, water pollution, and greenhouse gases. It supports sustainable agriculture and keeps the ecosystem healthy.
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Crop Yield Improvement | Increased productivity through targeted decision-making |
| Resource Efficiency | Optimized input usage and reduced waste |
| Sustainable Agriculture | Minimized environmental impact and long-term ecosystem health |
GIS helps farmers improve their work. It boosts crop yield improvement, resource efficiency, and sustainable agriculture. This leads to a better future for farming.
Challenges and Limitations of GIS in Farming
GIS technology has changed farming a lot. But, it comes with its own set of problems. The biggest issues are getting data to work together and the high cost of starting up.
Data Integration Issues
One big problem with GIS in agriculture is mixing data from different places. Farmers find it hard to put together data from sensors, satellites, and farm software. This makes it tough to make good decisions and improve farming.
High Implementation Costs
Starting with GIS technology costs a lot of money. The upfront cost of equipment, software, and training is high. Also, keeping it updated costs more, making it hard for small farms to join in.
To solve these problems, farmers and others need to work together. They should make GIS solutions easier to use and cheaper. Making data work together better and finding ways to pay for it can help more farms use GIS.
“The integration of GIS technology in agriculture is not without its hurdles, but the potential benefits outweigh the challenges. With continued innovation and collaboration, we can unlock the full potential of GIS to enhance agricultural productivity and sustainability.”
Future Trends of GIS in Agriculture
The world of agriculture is changing fast. New technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are set to change farming. GIS in agriculture is getting even better, thanks to new remote sensing tech.
Integration with IoT and AI
GIS and IoT are teaming up. IoT sensors and devices send real-time data on farms, like soil moisture and crop health. This data helps farmers understand their land better. They can then make smart, AI-powered farming choices.
Advancements in Remote Sensing Technologies
New advanced remote sensing tech is key for GIS in agriculture. Satellites, drones, and other aerial tools are getting better. They give farmers detailed, multispectral data. This data helps farmers watch crop growth, spot diseases, and predict yields.
These new IoT in agriculture and remote sensing techs are making farming better. Farmers can use these tools to grow more food and protect the environment.
“The integration of GIS, IoT, and AI will enable farmers to make data-driven decisions that optimize resource usage, increase yields, and promote environmental sustainability.”
| Technology | Benefit |
|---|---|
| IoT-powered Sensors | Real-time data collection on soil, weather, and crop conditions |
| AI-powered Analytics | Predictive models for crop management and yield forecasting |
| Advanced Remote Sensing | High-resolution spatial data for precision farming techniques |
Case Studies Showcasing GIS Impact
GIS has changed agriculture in amazing ways. By looking at real success stories, we learn a lot. These stories help farmers and experts all over the world.
Success Stories from Different Regions
In the Midwestern United States, a family farm used GIS to improve their farming. They looked at soil, weather, and past yields. This led to a 15% boost in corn and soybean production over three years.
In Australia, a big farm used GIS to find better land for crops. They mapped terrain, soil, and water. This found new areas for valuable crops, raising productivity by 20%.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
- GIS works best when it’s part of a bigger farming system.
- Farmers need training and support to use GIS well.
- Working together with GIS experts and local officials helps create better solutions.
These stories show how GIS can change farming. They improve productivity, manage resources, and increase profits. By learning from these examples, farmers can use GIS to improve their farms.
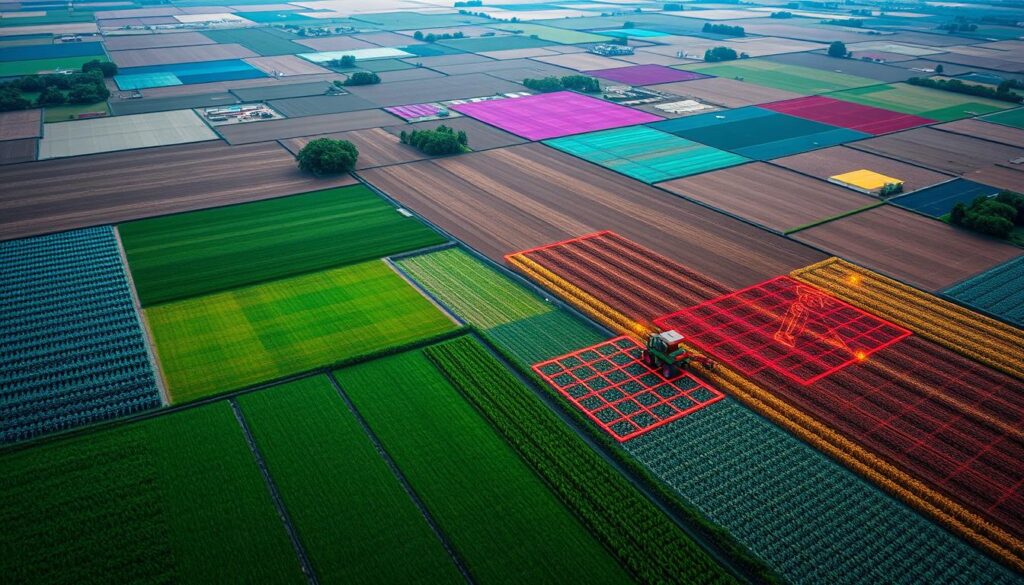

Conclusion and Recommendations
In this article, we’ve seen how Geographic Information Systems (GIS) change farming today. GIS helps farmers work more precisely and use resources better. It makes farming more productive and sustainable.
Summary of Key Points
GIS is key in making farming better. It offers many uses and brings big benefits like more crops and better use of resources. It also helps protect the environment. We talked about the challenges and the exciting future of GIS in farming.
Steps for Implementing GIS in Agriculture
To use GIS to its fullest in farming, follow these steps:
- Look at your farming methods and see where GIS can help.
- Get the right hardware, software, and data to use GIS.
- Train your team well so they can use GIS tools effectively.
- Work with GIS experts and research groups to learn new things.
- Keep updating your GIS plans to meet new challenges and opportunities.
By using GIS and following these steps, farmers and groups can do better. They can grow more food and take care of the environment. This helps everyone have enough to eat and keeps our planet healthy.