Deep Learning for Geospatial Image Analysis – Satellite Imagery
Deep Learning for Geospatial Image Analysis: Revolutionizing Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery has become an indispensable tool for understanding our planet, providing a wealth of information about land cover changes, natural disasters, and various environmental phenomena. But extracting meaningful insights from this vast data has long been a challenging task. Enter Geospatial Artificial Intelligence (GeoAI), powered by deep learning algorithms, which is transforming geospatial data analysis, particularly with satellite imagery.
Understanding GeoAI
GeoAI combines geospatial data with artificial intelligence techniques, enabling systems to leverage geographic context and analyze this data in a nuanced manner. At its core, GeoAI is heavily reliant on deep learning, a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn complex patterns and relationships from large datasets.
Key Features of GeoAI with Satellite Imagery
Deep learning’s capability has empowered GeoAI with several powerful features:
1. **Enhanced Classification Accuracy:** Traditional image classification techniques often struggled with satellite imagery’s inherent complexities, like accurately distinguishing tree species from each other. Deep learning is now able to accurately identify and classify different land cover types with high precision, even in challenging conditions like limited lighting or visible atmospheric interference.
2. **Automatic Object Detection:** Deep learning excels at identifying objects of interest within images, cutting down on tedious manual labeling and analysis. This capabilities allows for more efficient analysis, including identifying variations within an object over time, which can be crucial in understanding land use or crop health.
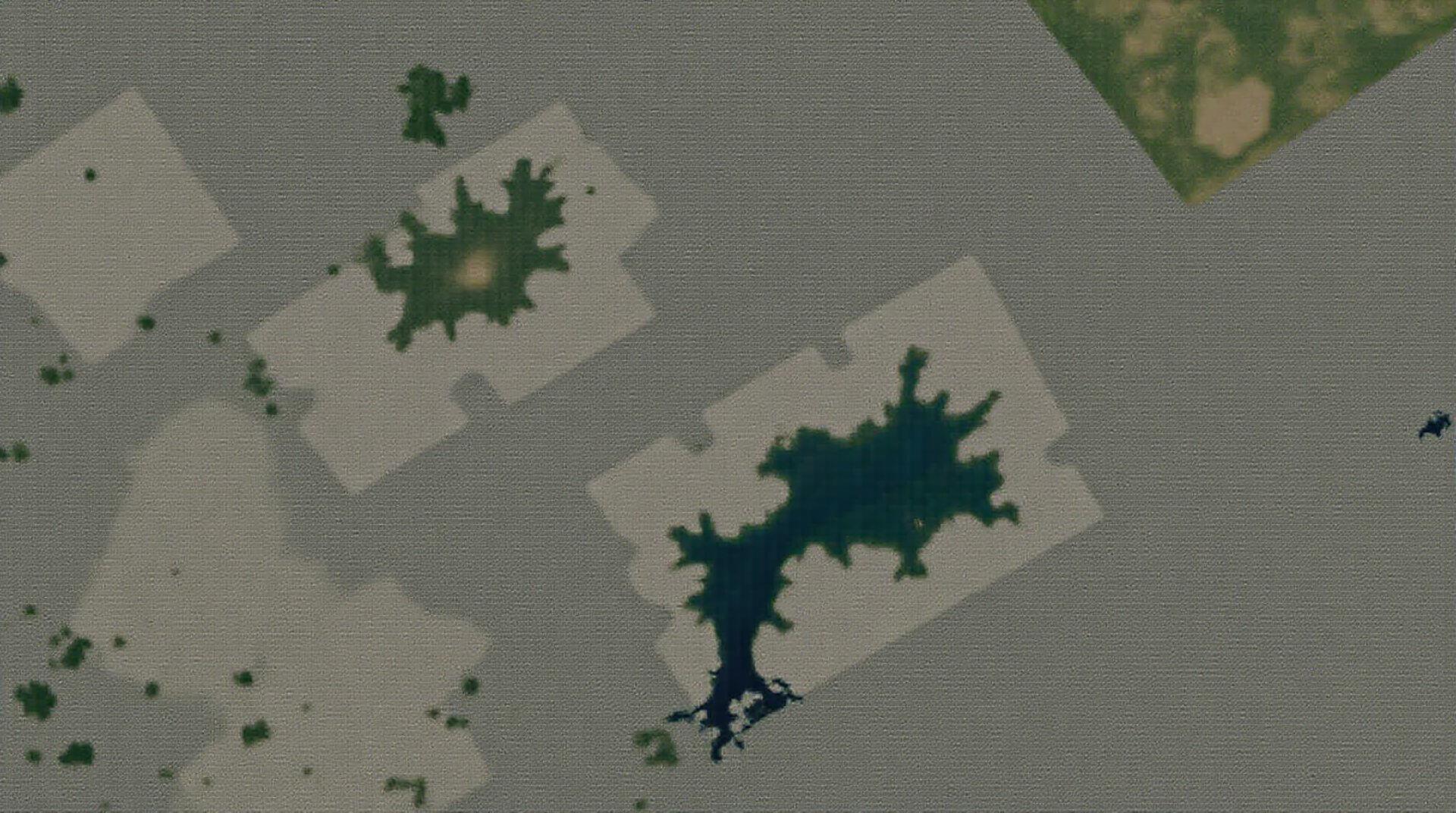
3. **Structural Change Detection:** GeoAI powered by deep learning can shine in detecting subtle changes over time, even within complex landscapes. This allows us to monitor deforestation, identify urban growth patterns, or detect and respond to emerging wildlife threats proactively.
4. **Multi-temporal Analysis:** By combining multiple satellite images taken over time, deep learning algorithms can uncover dramatic transitions in earth systems and provide valuable information about seasonal changes, human activity, and environmental shifts.
5. **Ecosystem Monitoring & Management:** Deep learning AI, combined with ground observations, can aid in monitoring and preserving biodiversity, identifying high-risk areas, and even predicting natural disasters.
Benefits of Using Deep Learning for Geospatial Image Analysis
* **Increased Efficiency & Accuracy:** Deep learning automates tasks previously requiring extensive human resources, boosting analysis speed and accuracy.
* **Enhanced Spatial Reasoning:** GeoAI can recognize spatial relationships within images, allowing for more sophisticated interpretations of data.
* **Reduced Costs & Dependence on Traditional Methods:** Deep learning can reduce the need for extensive ground observation and manual data interpretation, lowering costs and dependence on time-sensitive field work.
* **Improved Public Policy Decisions:** Accurate, timely data facilitated through GeoAI can guide more informed public policies related to land use, disaster preparedness, environmental management, and resource allocation.
Practical Applications
Some of the widely utilized applications of GeoAI-driven analysis include:
* **Urban Planning:** Detecting population growth, mapping urban sprawl, analyzing traffic patterns.
* **Climate Change Mitigation & Adaptation:** Monitoring deforestation, sea-level rise, and identifying vulnerable regions.
* **Disaster Relief & Response:** Assessing damage in the wake of earthquakes, floods, and other natural disasters.
* **Agricultural Advancements:** Precision farming, adjusting fertilizer and irrigation strategies based on soil and crop health analysis.
* **Environmental Monitoring:** Detecting pollution sources, tracking wildlife populations, managing biodiversity.
Resources for Learning and Exploring GeoAI in Geospatial Image Analysis
* **Kaggle Datasets:** https://www.kaggle.com/datasets
* **GeoAI Resources at the University of Maryland:** https://www.igis.umd.edu/research/geoai
* **Google Earth Engine:** https://developers.google.com/earth-engine
* **OpenStreetMap:** https://www.openstreetmap.org/
By utilizing the dynamic technology of deep learning, GeoAI promises a new era of geospatial analysis, delivering actionable insights and impacting various sectors to address a changing world.
## Deep-Learning-Geo-spatial Image Analysis: FAQs
**What is Deep-Learning-Geo-spatial Image Analysis?**
Deep-learning-geo-spatial image analysis is a field using artificial intelligence to analyze and extract information from geospatial images, like satellite or aerial photos. It leverages deep learning algorithms, specifically neural networks, empowered with large datasets to identify patterns, classify objects, and generate predictions within images overlaid onto geographical contexts.
**How does it work?**
Deep learning analyses images using layers of artificial neural networks that learn complex features and relationships within the images. Through training on vast datasets of labeled images, these networks can recognize different objects, patterns, and even subtle variations within geographical contexts.
**What types of geospatial images can it analyze?**
Deep learning can analyze a vast array of geospatial images, including:
* Satellite images
* Aerial photography
* Multispectral imagery
* Hyperspectral imagery
* LiDAR scans
* RADAR imagery
**What can it do?**
Deep learning-geo-spatial image analysis can perform various tasks, including:
* **Image classification:** Identifying different objects in the image like land use, vegetation, and water
* **Object detection:** Pinpointing specific objects, like cars, buildings, or trees
* **Change detection:** Analyzing differences between images over time, revealing changes in land use, deforestation, or urban development
* **Anomaly detection:** Identifying unusual or abnormal patterns within imagery to identify potential issues like crop stress or infrastructure damage
* **Remote sensing applications:** Predictive modeling of erosion, forest fires, and disaster assessments
**What formats are used can it work with?**
Deep learning models primarily require specific formats, such as:
* **Geospatial Databases:** Storing geospatial information like coordinates, geometry, and attributes in compatible formats like Shapefiles (.shp), GeoJSON (.geojson), or geor referenced databases.
* **Image Formats:** Deep models work well with popular image formats like PNG, JPEG, and TIFF, which are commonly used for geospatial image storage and transfer.
## Deep-Learning-Geo-spatial Image Analysis – Key Benefits
**Why is this so important?**
Deep-learning-geo-ospatial image analysis offers a range of benefits across various sectors:
* **Intelligent analysis:** Speeds up and enhances analyzes of large datasets, making current methods of analysis inefficient.
* **New insights:** Extracts new knowledge from geographically referenced data to aid decision-making.
* **Efficiency**: Enables efficient mapping and monitoring of resources, infrastructure, and environments.
**Actions You Can Take:**
For further exploration, visit: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/article/deep-learning-and-the-future-of-geo-spatial-data
**Conclusion:**
Deep learning-geo-spatial image analysis is revolutionizing the way we utilize geospatial data. By leveraging highly visual, complex, data-heavy images, AI models can uncover intricate relationships and identify patterns invisible to the human eye. This opens up numerous possibilities for professional and academic exploration across diverse fields, from agriculture to disaster management and environmental conservation. Continued research and development in this domain are vital to unlock further benefits of deep learning in combining spatial analysis with AI’s power, enabling smarter and more effective decision-making for the better future.