Geospatial Modeling and Mapping
Table of Contents
Introduction to geospatial mapping
In today’s fast-changing digital world, geospatial modeling and mapping are key. This article will dive into the latest in GIS, remote sensing, and 3D visualization. It aims to help professionals in many fields use spatial data to change things for the better.
This article will show you how to work with geospatial data and make detailed models and visuals. It’s for anyone interested in how the world works, from urban planners to natural resource managers. You’ll learn a lot about geospatial modeling and mapping and how to apply it.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the fundamentals of geographic information systems (GIS) and their transformative potential
- Discover the latest advancements in geospatial data collection techniques
- Explore comprehensive approaches to geospatial modeling and spatial data analysis
- Learn about the diverse mapping technologies and applications shaping various industries
- Gain insights into the role of geospatial modeling and mapping in environmental and urban planning
Introduction to Geospatial Modeling and Mapping
Understanding the Fundamentals of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are key in the world of spatial analysis. They help manage, analyze, and show geospatial data. This technology has changed many industries, like urban planning and natural resource management.
GIS combines data from satellites, GPS, and demographics to create detailed maps. It lets experts find patterns and make smart choices. These choices help our communities and the environment grow.
A GIS system has three main parts: collecting data, creating models, and analyzing it. These parts work together to show complex relationships and create maps. These maps help share important findings clearly.
The use of GIS is growing in many fields. It’s used in urban planning and managing natural resources. This technology is changing how we solve problems and analyze spaces.
Geospatial Data Collection Techniques
Getting accurate and current geospatial data is key for any project. This part looks at how we collect this data. We use remote sensing, LiDAR, and GPS surveys for this.
Remote Sensing: Eyes in the Sky
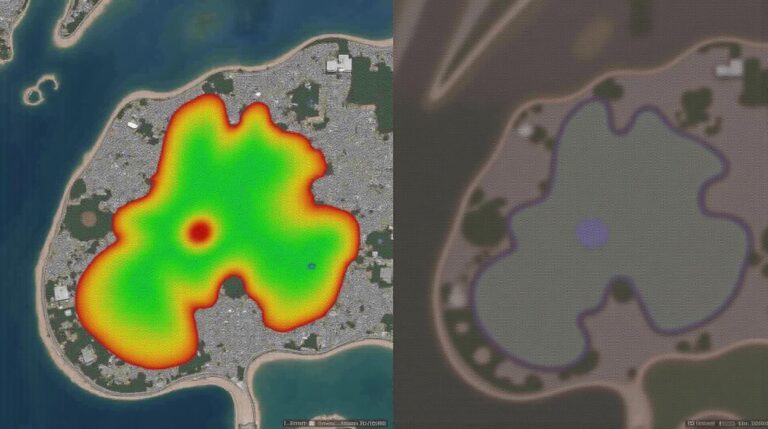
Remote sensing is a big part of getting geospatial data. It uses sensors in the air or on satellites to study the Earth. It can take pictures, infrared data, and even 3D models of the ground.
Precision with LiDAR
LiDAR is a laser method that gives super accurate data. It shoots out light pulses and makes detailed 3D models of landscapes and buildings. It’s very useful for many tasks.
GPS: Mapping the World
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is key for mapping and tracking. It helps plan infrastructure, manage resources, and respond to emergencies. GPS works well with other tech to get important data.
| Method | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Sensing | Broad spatial coverage High-resolution imagery Ability to capture infrared and 3D data | Potential for cloud cover or atmospheric interference Limited ability to capture ground-level details |
| LiDAR | Highly accurate 3D data Ability to penetrate vegetation Detailed terrain mapping | Relatively high cost of equipment and data processing Limited coverage area per survey |
| GPS | Precise location tracking Widespread availability of GPS devices Integration with other geospatial technologies | Potential for signal interference in dense urban or forested areas Dependency on satellite coverage and availability |
Knowing the good and bad of these methods helps us choose the best for our projects. This way, we can get the data we need.
Geospatial Modeling: A Comprehensive Approach
Geospatial modeling is a powerful tool for understanding our world. It uses advanced techniques to analyze and interpret spatial data. This helps us find patterns and insights for many applications.
Spatial Data Analysis and Visualization
At the core of geospatial modeling is spatial data analysis. We use complex algorithms to find important information in geographic data. This method helps us uncover the stories hidden in our data.
Data visualization is key to sharing these insights. It makes complex spatial information easy to understand. This helps everyone, from decision-makers to the public, grasp the world’s patterns and relationships.
| Technique | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Spatial Modeling | Urban planning, resource management, transportation optimization | Identify patterns, predict trends, and support informed decision-making |
| Spatial Analysis | Epidemiology, environmental monitoring, site selection | Uncover hidden relationships, assess spatial interdependencies, and optimize resource allocation |
| Data Visualization | Public policy, climate change research, market analysis | Effectively communicate complex spatial information, enhance understanding, and drive impactful decisions |
“Geospatial modeling is not just a tool, but a lens through which we can see the world in a new and enlightening way, unlocking the hidden stories that shape our lives and our planet.”
Many software are used to manipulate Geospatial data, such as QGIS (Free open-source software www.qgis.org) and ArcGIS ( https://esri.com).
Find more about top GIS software in our previous post Here :
Mapping Technologies and Applications
Geospatial mapping has seen big changes, changing how we see and use our world. From simple 2D maps to detailed 3D ones, these new tools are used in many fields. They help us plan, manage, and understand our surroundings better.
2D and 3D Mapping for Diverse Industries
2D maps are still key, showing us what places look like from above. They help with city planning, roads, and buildings. They help experts make smart choices and use resources well.
3D mapping takes it up a notch, showing us the world in depth. It uses height data to show us the world in 3D. This tech is used in real estate, building, saving nature, and helping after disasters. It helps us make better choices and understand our world better.
| Industry | 2D Mapping Applications | 3D Mapping Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Urban Planning | Land-use analysis Transportation planning Infrastructure management | Visualizing urban development Modeling building structures Assessing environmental impact |
| Natural Resource Management | Forestry monitoring Agricultural planning Conservation efforts | Terrain analysis Ecosystem modeling Habitat preservation |
| Disaster Response | Emergency planning Damage assessment Evacuation routing | 3D visualization of affected areas Identifying high-risk zones Coordinating rescue operations |
As 2D mapping and 3D mapping get better, GIS uses grow. This changes many fields and how we see and use our world.
Geospatial Modeling and Mapping: Shaping the Future
The world of geospatial technology is on the verge of big changes. These changes will change how we see, analyze, and interact with our surroundings. Key trends include artificial intelligence, cloud-based platforms, and real-time data analysis.
Artificial intelligence is changing geospatial modeling and mapping. It helps us find deeper insights, automate tasks, and make accurate decisions. AI and geospatial tech together will improve urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster response.
Cloud-based geospatial platforms are also on the rise. They make data integration, teamwork, and scalable computing easy. This makes geospatial analysis available to more people, making the field more open and inclusive.
Real-time data analysis is becoming more important. Geospatial experts can now use live data, satellite images, and crowdsourced info for quick insights. This helps us respond fast to environmental changes, disasters, and city growth.
Looking forward, the future of geospatial modeling and mapping is exciting. By adopting these trends and technologies, we can solve global problems and create a better future for everyone.
Environmental and Urban Planning with GIS
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are key in environmental and urban planning. They help planners and researchers solve big problems better. These tools make it easier to understand and manage our world.
In environmental planning, GIS changes how we use land and manage resources. It helps us find the best ways to use land and protect ecosystems. This way, we can make better choices about our environment.
GIS also changes urban planning. It lets us see how cities will grow and how to make them better. We can plan for more people, better roads, and stronger buildings. This makes cities better places to live.
| Application | GIS Capabilities | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Planning | Spatial data integration Land-use optimization Ecosystem monitoring Disaster risk modeling | Sustainable resource management Informed decision-making Improved environmental resilience |
| Urban Planning | Demographic analysis Transportation planning Infrastructure optimization Scenario-based modeling | Livable, sustainable cities Efficient resource allocation Enhanced urban resilience |
The need for environmental GIS, urban planning, and spatial planning will keep growing. GIS will help us make our world better. It’s key for a sustainable future for all.
Geospatial Modeling in Natural Resource Management
Geospatial modeling and mapping are changing how we manage natural resources. They are key in forestry, agriculture, and conservation. These tools help us make better decisions for our planet.
Forestry: Optimizing Sustainable Practices
Geospatial modeling is crucial for sustainable forestry. It uses Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to track forest health. This helps in deciding when to harvest timber and how to protect ecosystems.
It also helps in using resources wisely. This way, we can reduce harm to the environment and increase productivity.
Agriculture: Precision Farming Innovations
In agriculture, geospatial modeling is a game-changer. It uses GIS and remote sensing to monitor soil, water, and pests. This info helps farmers plan better, like when to water and fertilize.
It leads to better crops and more efficient farming. This is good for the planet and for farmers.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting Vulnerable Ecosystems
Geospatial modeling is vital for conservation. It helps find and watch over fragile ecosystems. By mapping plants and animals, we can protect their homes and stop harm.
It also helps us understand how climate change affects these areas. This knowledge guides us in making our conservation efforts better.
Geospatial modeling is a beacon of hope for natural resource management. It gives us the tools to tackle big challenges with care and precision.
Advances in Geospatial Modeling and Mapping
The field of geospatial technology is changing fast. This is thanks to new technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Cloud-based platforms are also playing a big role. These changes are making it easier to collect, analyze, and use data.
AI and machine learning are big deals in geospatial modeling and mapping. They help automate complex tasks. This means we get insights faster and more accurately. For instance, AI can spot land use changes, find urban patterns, and predict disaster impacts better.
Cloud-based data integration platforms have also changed the game. They let us share and access geospatial data easily. These platforms can handle data from satellites, sensors, and more. This helps us understand complex issues better.
| Advancement | Impact |
|---|---|
| AI and Machine Learning | Automation of spatial analysis tasks, improved accuracy and speed of insights |
| Cloud-based Data Integration | Real-time processing, seamless integration of diverse data sources |
| Sensor Technology | Enhanced data collection, real-time monitoring of environmental and infrastructure changes |
Sensor technology has also changed how we collect data. We now have more data than ever before. This data, combined with geospatial technology, helps us make better decisions. We can track changes in real-time.
“The future of geospatial modeling and mapping lies in the seamless integration of diverse data sources, powered by the latest advancements in AI, machine learning, and cloud-based technologies.”
The geospatial industry is always growing. It has huge potential in areas like urban planning and natural resource management. By using these new technologies, we can make a better future.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in GIS
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are becoming more popular. But, they face unique challenges and ethical issues. These include data privacy and the risk of biased decisions. Using GIS wisely requires careful thought.
Data privacy is a big challenge in GIS. The use of location-based data can threaten personal privacy. GIS experts must find a balance between using data wisely and protecting personal info.
Bias in GIS is another major issue. The data and algorithms used can reflect and worsen existing biases. This can lead to unfair decisions for some groups. It’s crucial to understand GIS’s ethical side and aim for fairness.
The environmental impact of GIS is also important. The tech uses a lot of energy and resources. It can also be misused to harm the environment. We need to use GIS in a way that’s good for the planet.
“Responsible GIS practices require a multifaceted approach that prioritizes data privacy, mitigates algorithmic bias, and minimizes environmental impact.”
To tackle these issues, GIS experts need to follow ethical guidelines. They should focus on being open, accountable, and caring for people and the planet. This way, GIS can help us for the better, while being responsible.
Conclusion
Geospatial modeling and mapping are key to understanding and managing our world. They use Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and advanced data analysis. This field has changed how we tackle complex issues in many industries.
The future of geospatial modeling and mapping looks bright. New technologies like satellite imagery and cloud computing will help us find new insights. People in fields like environmental planning are using these tools to solve big problems and make our future sustainable.
This article has shown how powerful geospatial modeling and mapping are. We’ve seen how they are changing our world today and will shape it tomorrow. As these technologies grow, they will be crucial for our planet’s future. Learning to use them well is more important than ever.
FAQ
What is geospatial modeling and mapping?
Geospatial modeling and mapping use Geographic Information Systems (GIS). They help create, analyze, and show spatial data. This includes many techniques and tools for managing and understanding geographic information. It supports decision-making in different fields.
What are the core components of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)?
GIS has several key parts. These include collecting data (like remote sensing and GPS), spatial models, and data storage. It also includes analysis and visualization tools. GIS combines different data sources to create detailed geographic information.
What are the key geospatial data collection techniques?
Main data collection methods are remote sensing, LiDAR, and GPS surveys. These provide accurate and current spatial data. They are used in many applications.
How are geospatial models used for spatial data analysis and visualization?
Geospatial modeling prepares data, applies analysis algorithms, and uses predictive models. It finds patterns and relationships in geographic data. Good data visualization is key to sharing these insights with others.
What are the applications of 2D and 3D mapping technologies?
2D and 3D mapping is used in many areas. This includes urban planning, transportation, and environmental conservation. These tools help understand the environment and support smart decisions.
What are the emerging trends and future developments in geospatial modeling and mapping?
Geospatial technology is growing fast. It’s driven by AI, cloud platforms, and real-time data. These changes are changing how we collect, analyze, and use spatial data. They help solve global problems and drive innovation.
How is geospatial modeling used in environmental and urban planning?
Geospatial modeling is key in environmental and urban planning. It helps tackle challenges like sustainable land use and disaster risk. GIS is a valuable tool for making informed decisions and planning.
What are the applications of geospatial modeling in natural resource management?
Geospatial modeling is vital for managing natural resources. It includes forestry, agriculture, and conservation. Spatial data and advanced techniques help monitor ecosystems and support environmental efforts.
What are the ethical considerations and challenges in GIS?
Geospatial modeling and mapping have benefits but also challenges. These include data privacy, biased decisions, and environmental impact. It’s important to address these issues for responsible use of geospatial technology.



6 Comments