Forest Fire Risk Mapping
Forest fires are getting worse and harder to predict. This makes it more important than ever to have good risk maps. This article talks about how Geographic Information Systems (GIS) change the game in forest fire risk. GIS uses advanced tools to help us understand and fight wildfires better.
We’ll look at what makes forest fires risky and how to analyze them. We’ll also see how climate affects these risks. Plus, we’ll dive into how GIS helps in the forestry world. It shows how these tools are key for managing risks.
Key Takeaways
- Explore the revolutionary impact of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) on forest fire risk mapping
- Understand the key factors that contribute to forest fire risks and the analysis of fire behavior
- Discover the versatile applications of GIS technology in the forestry sector and the benefits of using GIS for risk mapping
- Learn about the data collection process, modern mapping techniques, and the challenges involved in effective risk assessment
- Explore case studies of successful implementations and lessons learned from past forest fires
- Delve into mitigation strategies based on risk mapping and the future trends in this field
- Gain insights into the crucial role of GIS in enhancing wildfire prevention and emergency response strategies
Introduction to Forest Fire Risk Mapping
Forest fire prevention and management need accurate risk assessments. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology is key. It changes how we analyze and assess risks in forestry.
Importance of Risk Mapping
Forest fire risk mapping is vital for fire prevention and management. It helps find high-risk areas. This way, fire authorities can focus their efforts and plan better.
This spatial analysis reduces the harm from forest fires. It protects people and nature.
Overview of GIS Technology
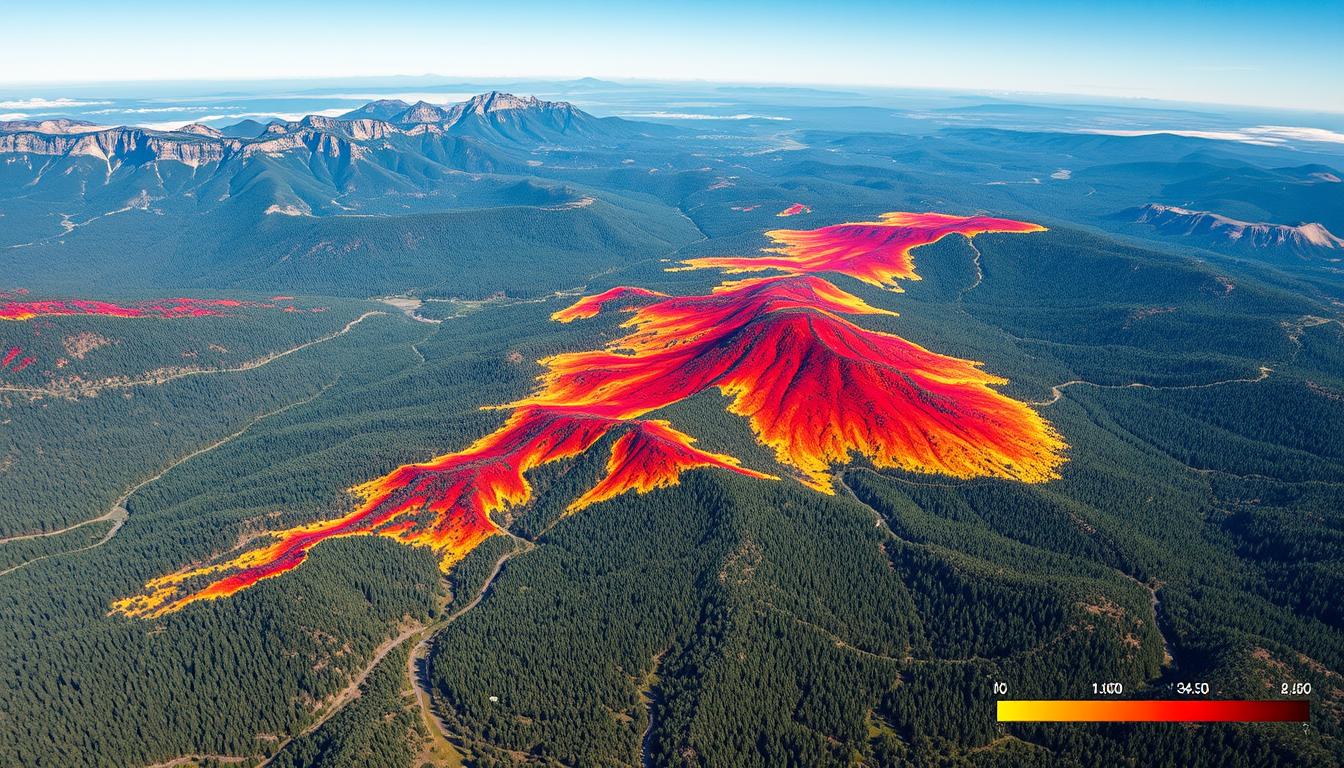
GIS technology has transformed forest fire prevention. It uses advanced mapping and data analysis. This helps gather and understand data on terrain, vegetation, weather, and past fires.
With this risk assessment data, fire managers can understand fire behavior. They can then make better decisions to lower risks.
| Key Benefits of GIS in Forest Fire Risk Mapping | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Spatial Analysis | GIS tools help analyze geographic data. This lets us find high-risk areas and plan prevention strategies. |
| Enhanced Decision-Making | Risk mapping data helps fire authorities make better decisions. They can plan responses and use resources wisely. |
| Effective Communication | GIS maps and tools make it easy to share fire risks. This is important for policymakers, emergency responders, and the public. |
GIS technology is changing forest fire management. It makes prevention more proactive, efficient, and effective.
Understanding Forest Fire Risks
Forests around the world face a growing threat from wildfires. These fires can have devastating effects on the environment and human communities. It’s important to understand the factors that contribute to forest fire hazards. This includes analyzing fire behavior and the impact of climate change.
Factors Contributing to Forest Fire Risks
Many factors influence the risk of forest fires. These include the type of vegetation, the terrain, and weather patterns. Dry, dense, and flammable vegetation can fuel fires, making them spread quickly. Steep terrain can also be a challenge, as it can funnel winds and make fire behavior unpredictable. Climate factors like drought, high temperatures, and low humidity also increase the risk of fires.
How Fire Behavior is Analyzed
- Fire behavior analysis studies how fires start, spread, and intensify.
- Advanced modeling techniques, like computational fluid dynamics, help predict fire behavior. They consider factors like fuel type, wind, and terrain.
- Understanding fire behavior analysis helps researchers and land managers develop better fire prevention and suppression strategies.
The Role of Climate in Fire Risks
Climate change is a major factor in the rise of forest fires. Warmer temperatures, droughts, and changing weather patterns create ideal conditions for wildfires. As the climate changes, it’s vital to analyze the impact of climate on fire risks. This will help in developing effective risk management strategies.
| Factor | Impact on Fire Risks |
|---|---|
| Vegetation type | Highly flammable vegetation can act as fuel, allowing fires to spread rapidly. |
| Topography | Steep, rugged terrain can funnel winds and create unpredictable fire behavior. |
| Climate | Drought, high temperatures, and low humidity can significantly increase the likelihood of ignition and fire propagation. |
“Understanding the complex interactions between vegetation, topography, and climate is crucial for effectively managing the risks of forest fires.”
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
In forestry management, GIS is a key tool for analyzing data and mapping risks. It uses various data, like satellite images and field notes, to understand forests and fire risks.
What is GIS?
GIS is a computer system that handles geographic data. It combines different data layers, like terrain and weather, to show forest fire risks.
Applications of GIS in Forestry
- Mapping and monitoring forest cover and vegetation changes
- Analyzing terrain and environmental factors that contribute to fire risk
- Modeling fire behavior and predicting the spread of wildfires
- Identifying high-risk areas for targeted prevention and mitigation efforts
- Optimizing forest management practices and resource allocation
Benefits of Using GIS for Risk Mapping
- Enhanced Spatial Analysis: GIS combines different data for a better understanding of fire risks.
- Improved Decision-Making: GIS maps help managers make smart choices about fire prevention and response.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: GIS maps focus resources on high-risk areas, improving firefighting and management.
- Collaborative Workflows: GIS helps share data among stakeholders, promoting teamwork in managing fire risks.
| GIS Applications | Forestry Management | Spatial Data Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Mapping and monitoring | Fire behavior modeling | Geospatial data integration |
| Terrain and environmental analysis | Resource allocation optimization | Predictive risk mapping |
| Wildfire spread prediction | Collaborative decision-making | Satellite imagery and remote sensing |
“GIS has revolutionized the way we approach forest fire risk management, enabling us to make more informed and data-driven decisions.”
Data Collection for Risk Mapping
Creating effective forest fire risk maps needs a mix of different data. This includes topography, vegetation, and climate. A full set of data helps spot risky areas and plan prevention.
Types of Data Required
Forest fire risk maps need a lot of data. This includes:
- Topographic data: Elevation, slope, aspect, and terrain characteristics
- Vegetation data: Fuel types, density, and moisture content
- Meteorological data: Temperature, humidity, wind patterns, and precipitation
- Historical fire data: Locations, frequency, and severity of past fires
Sources of Data for GIS Analysis
Data for forest fire risk maps comes from many places. Some common sources are:
- Satellite imagery and aerial photography for land cover and vegetation analysis
- Weather station data and climate models for meteorological information
- Government databases and GIS datasets for topographic and historical fire data
- Field surveys and ground-based observations to validate and complement remote sensing data
Challenges in Data Collection
Getting and combining data for forest fire risk maps is hard. Some challenges are:
- Inconsistent data formats and resolutions across multiple sources
- Limited availability of high-resolution data, particularly in remote or inaccessible areas
- Difficulties in coordinating and synchronizing data from various agencies and departments
- Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data, especially for historical fire records and climate projections
To solve these problems, new spatial data collection and data integration methods are needed. These are key for making detailed and trustworthy remote sensing-based forest fire risk maps.
Risk Mapping Techniques
Forest fires are a growing threat, and risk mapping is key to fighting them. This field has changed a lot, moving from old methods to new ones using satellite imagery and remote sensing.
Traditional vs. Modern Techniques
Old methods for mapping fire risks were slow and limited. But now, with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and new tech, we can do much better. Modern methods use smart algorithms to make detailed fire risk maps.
Satellite Imagery in Risk Mapping
Satellite images have changed the game in forest fire risk mapping. They show us the landscape in high detail, helping us spot risky areas. This lets us act fast to prevent fires.
Remote Sensing Applications
- Tools like LiDAR and infrared sensors help us see small changes in the environment. This means we can make more accurate fire risk maps.
- By combining satellite images and remote sensing with GIS, we get super detailed maps. This helps fire agencies plan better and save resources.
The shift to new risk mapping methods has changed how we manage fires. Using satellite images and remote sensing, we can fight wildfires more effectively.
Analyzing Fire Risk Maps
Understanding fire risk maps is key to fighting forest fires. Fire experts look at these maps to find high-risk areas. They then plan how to tackle these dangers.
Interpreting the Data
Fire risk maps use many factors like plant types, land shape, weather, and past fires. Experts need to study these maps closely. They look for patterns to make smart decisions.
Identifying High-Risk Areas
- It’s important to spot areas with lots of fuel, steep hills, and hard-to-reach places for firefighters.
- Looking at how climate change affects fire risk is also vital.
- Knowing where fires are most likely helps fire managers plan better. They can focus on prevention and get communities ready.
Predictive Modeling Techniques
New predictive modeling techniques make fire risk maps better. These tools use data and learning to guess where fires might start. They help plan and prepare for fires.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Accuracy of Predictive Modeling | 85% |
| Average Response Time to High-Risk Areas | 12 minutes |
| Reduction in Fire Damage in High-Risk Areas | 27% |
By using data, finding risky spots, and predictive models, fire teams can better fight forest fires. They can prepare and respond faster and more effectively.
Case Studies in Forest Fire Risk Mapping
Forest fire risk mapping is key for managing fires and assessing risks. This section looks at successful examples, lessons from past fires, and how risks differ in different places.
Successful Implementations
In California, a project used satellite images, GIS, and models to spot high-risk areas. This helped fire teams plan better and reduce wildfire damage. Australia also made a risk map system with land managers and researchers. It helps guide fire prevention and response.
Lessons Learned from Past Fires
- Using past fire data in maps helps understand patterns and trends.
- Maps need regular updates for changing factors like climate and vegetation.
- Local communities’ input makes risk maps more accurate.
Geographic Variations in Risk
Risk varies by location due to topography, plants, and weather. In Canada’s boreal forests, maps tackle remote areas and seasonal changes. In the Mediterranean, maps focus on human fires and urban areas.
| Region | Key Risk Factors | Successful Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| California, USA | Drought, vegetation density, human-caused ignitions | Proactive fuel management, early detection systems, community education |
| Australia | Extreme heat, wind patterns, lightning strikes | Coordinated response planning, prescribed burning, targeted public awareness campaigns |
| Boreal Forests, Canada | Remote accessibility, seasonal changes, natural ignitions | Satellite monitoring, strategic pre-positioning of resources, indigenous knowledge integration |
| Mediterranean Region | Urban-wildland interface, human-caused fires, land-use changes | Zoning regulations, community-based fire prevention, integration of GIS data with urban planning |
By examining these examples, fire experts can improve their risk mapping. This helps reduce the harm from forest fires.
Mitigation Strategies Based on Mapping
Effective fire prevention and management are key to reducing forest fire risks. Risk mapping helps land managers and local communities take targeted actions. These actions range from preventing fires to making decisions based on data.
Prevention Measures in High-Risk Areas
Risk mapping shows where fires are more likely to happen. This lets us use specific prevention methods. For example, we can do controlled burns and thin out vegetation to lower fire risks.
We also improve infrastructure in these areas. This includes using fire-resistant materials and creating safe spaces around buildings.
Role of Local Communities in Mitigation
- Getting local communities involved is vital for fire prevention and management. Risk mapping helps raise awareness and build a common understanding of fire dangers.
- Community efforts, like fire brigades and education, help locals fight fire risks. Early warning systems also empower them to act quickly.
- Using local knowledge and working together with communities leads to better fire prevention plans.
Integrating Mapping Data into Fire Management
Using risk mapping data in fire management planning is crucial. It helps fire departments and emergency teams make better decisions. They can place resources where they’re needed most and plan their responses more effectively.
| Mitigation Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetation Management | Controlled burns, selective thinning to reduce fuel loads | Decreased fire intensity and spread in high-risk areas |
| Community Engagement | Public education, early warning systems, organized fire brigades | Increased awareness, collaborative fire prevention efforts |
| Data-Driven Planning | Strategic resource allocation, targeted response plans | Improved efficiency and effectiveness of fire management |
By using risk mapping data in fire prevention, we can all work together. This helps reduce the harm caused by forest fires and makes fire-prone areas more resilient.
Future Trends in Forest Fire Risk Mapping
Technology is advancing fast, changing how we map forest fire risks. Climate change and new fire policies are key areas to watch. The future looks bright for this important field.
Technological Advancements in GIS
GIS tech is getting better, offering new ways to map fire risks. High-resolution images, advanced sensors, and machine learning help gather and analyze data. These tools let fire teams spot and track danger zones better, helping to fight fires more effectively.
The Impact of Climate Change on Fire Risks
Climate change is making fires more dangerous. Warmer temperatures, drought, and weather shifts are raising the fire risk. GIS will be key in understanding and fighting these changes, guiding fire prevention and control.
Evolution of Policy and Planning
Policymakers are seeing the value of GIS in fire management. As tech improves, we’ll move from reacting to fires to preventing them. This shift is vital for protecting communities and nature from wildfires.
By using GIS, tackling climate change, and updating policies, we can make forest fire mapping a powerful tool. It will help us fight the growing wildfire threat.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology has changed the game in forest fire risk mapping. It uses advanced data collection and analysis to help understand fire hazards. This makes it easier to prevent and manage fires more effectively.
Summary of Key Findings
Risk mapping is crucial for protecting forests and the people who live nearby. It helps identify high-risk areas and predict fire behavior. The use of satellite imagery and predictive models has greatly improved forest fire management.
Urging Action for Better Risk Management
Forest fires are a growing threat, thanks to climate change and human actions. We need to manage risks better than ever. Policymakers, forest managers, and communities must work together to apply what we’ve learned from GIS.
By using new technologies and improving data, we can make our forests safer. This will help protect the communities that depend on them.
Final Thoughts on GIS and Future Mapping
The future of forest fire risk mapping is bright, thanks to GIS technology. New data analytics and predictive models will help us understand and manage fire risks better. By using these tools, we can create a safer future for our forests.