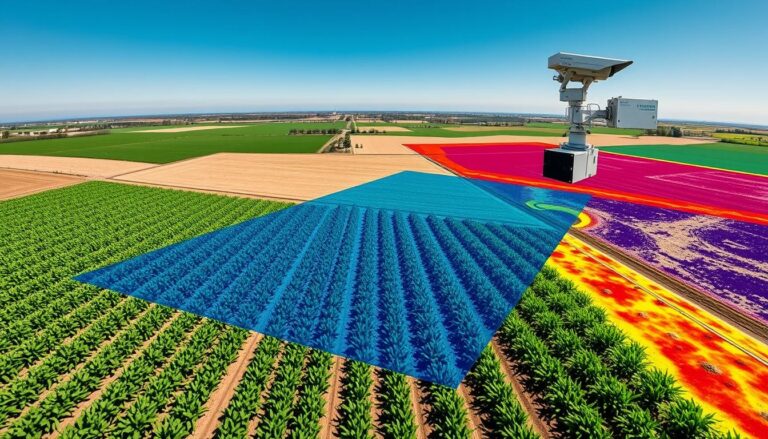
Mapping Urban Vegetation with Remote Sensing
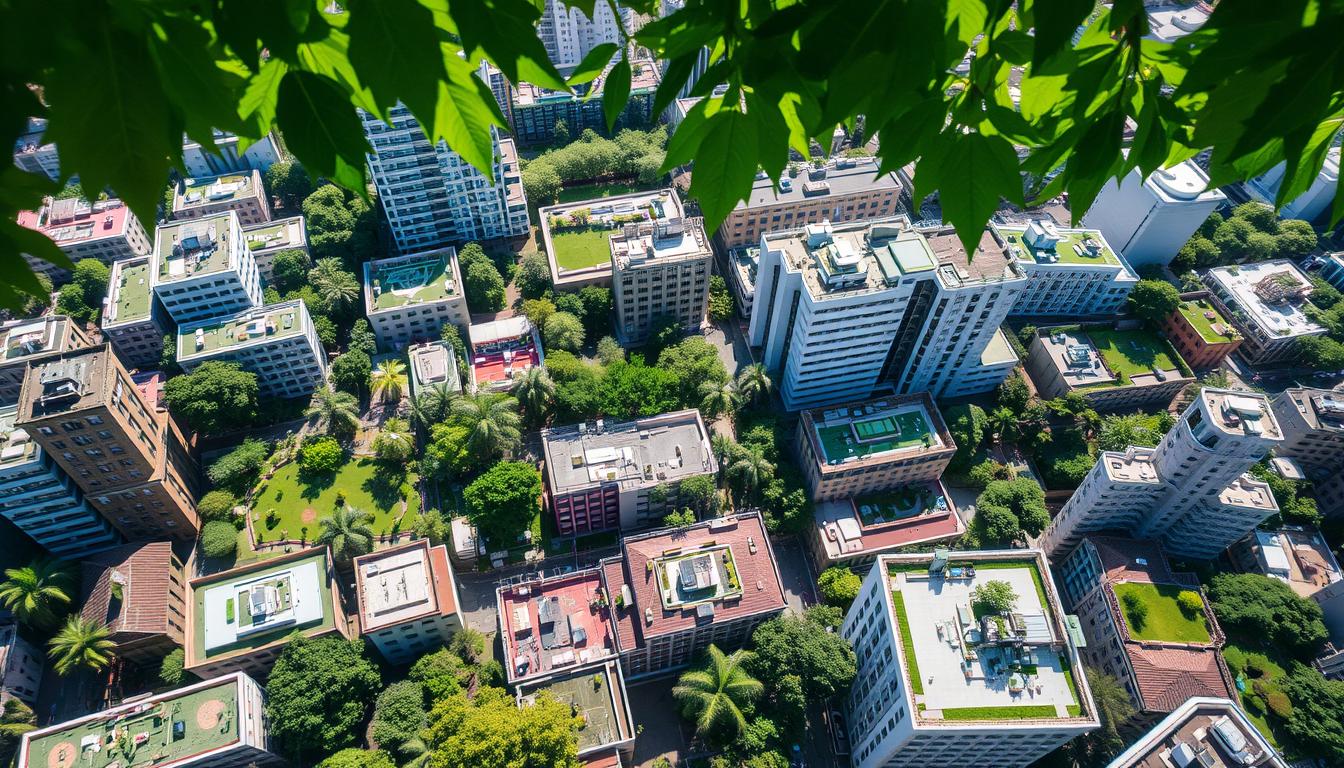
Remote sensing technology is key in mapping urban vegetation. It helps city planners and experts make cities better and greener. This tech lets us see how green spaces are doing, making cities healthier for everyone.
Remote sensing lets us study the Earth’s surface without touching it. It uses satellites and drones to collect data. This way, we can understand how green spaces work in cities better than ever before.
Knowing how green spaces change over time is very important. It helps solve big city problems like heat and keeping nature alive. This article talks about how remote sensing works and how it helps us make cities better.
Key Takeaways
- Remote sensing is a powerful tool for mapping and analyzing urban vegetation, providing valuable insights for urban planning and environmental management.
- Satellite imagery, aerial photography, and LiDAR technology are the primary remote sensing tools used to gather data on urban green spaces.
- Vegetation indices, classification methods, and change detection techniques are key analytical approaches in remote sensing for urban vegetation mapping.
- Remote sensing offers enhanced coverage, real-time monitoring, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional ground-based surveys.
- Challenges in remote sensing include data accuracy, interpretation complexity, and environmental factors affecting data quality.
Introduction to Remote Sensing
Remote sensing has changed how we study cities. It uses satellites and cameras in the air to collect data without touching the ground. This method is key for studying how plants grow in cities.
Definition and Concept
Remote sensing lets us get information from a distance. It uses special sensors to detect and analyze light from objects. This helps us understand cities better, including how plants are doing.
Importance in Urban Studies
Remote sensing has made studying cities better. It gives a clear view of the city from above. This helps us see how plants are doing and how they change over time.
This info is vital for making cities greener and more sustainable. It helps us plan better for the future.
“Remote sensing has revolutionized the way we study and manage urban environments, providing us with unprecedented access to data that was once difficult to obtain.”
As more people move to cities, remote sensing becomes even more important. It’s a way to watch over and manage city plants. This helps make cities better places to live.
The Role of Remote Sensing in Urban Ecology
Remote sensing technology has greatly helped urban ecology. It uses satellite images and aerial photos. This helps urban planners and ecologists understand our cities better.
This knowledge is key for better urban ecology, ecosystem services, and green infrastructure.
Understanding Urban Ecosystems
Remote sensing gives a bird’s-eye view of cities. It helps map different land types like plants, buildings, and water. This is crucial for seeing how nature and buildings interact in cities.
By studying changes in plants, researchers learn about urban health and strength.
Benefits for Urban Planning
Remote sensing data helps in urban planning. It shows where cities need more green spaces. This helps plan new parks and gardens.
It also checks if current green projects work well. This feedback helps improve future plans.
| Application | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Mapping urban vegetation | Identify areas for potential green space expansion |
| Monitoring urban heat island effects | Develop targeted strategies to mitigate urban heat |
| Assessing ecosystem services | Understand the value of urban greenery and guide conservation efforts |
Remote sensing gives urban planners valuable insights. They can make better decisions for a greener, healthier city.
Technologies Used in Remote Sensing
Remote sensing technologies are key in mapping urban green spaces. They offer a detailed look at city vegetation. The main tools are satellite imagery, aerial photography, and Lidar technology.
Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery is crucial for studying urban plants. Satellites like Landsat, Sentinel, and MODIS give us high-resolution views. They help us see where plants are and what they look like.
By looking at plant colors, scientists can map out city greenery. This helps city planners manage green spaces better.
Aerial Photography
Aerial photos give us a close-up view of cities. They come from planes or drones. This method shows more detail than satellites, like individual trees and parks.
It also lets us track changes in plants over time. This helps us understand how cities affect the environment.
Lidar Technology
Lidar uses laser light to create 3D maps of areas. It’s great for mapping urban plants. It shows how tall and dense plants are.
This info helps in planning cities. It guides where to build and how to manage green areas.
Using all these technologies together gives us a full picture of city plants. It helps us make cities greener and more sustainable.
Data Sources for Urban Vegetation Mapping
Getting accurate data is key for good urban vegetation maps. Remote sensing has changed how we gather and use data on city greenery. MODIS, Landsat, and Sentinel satellites are main sources for this work.
MODIS Data
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is a satellite sensor that covers the globe well. It’s great for tracking big changes in city plants over time. MODIS gives us a long-term view.
Landsat Program
The Landsat program is a team effort between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. It’s a top choice for mapping city plants. Landsat’s data is high quality and has a long history, helping us see city plants at different levels.
Sentinel Satellites
The Sentinel satellites are part of the Copernicus program by the European Space Agency (ESA). They have special sensors and better detail for city plant maps. Sentinels give us deep insights into city plants.
These different data sources help us understand city plants better. By using remote sensing data from these sources, we can plan better for green cities and protect the environment.
Techniques in Remote Sensing Analysis
Remote sensing is key for mapping and watching over urban greenery. It uses three main methods: vegetation indices, image classification, and change detection. These tools help us understand urban green spaces better.
Vegetation Indices
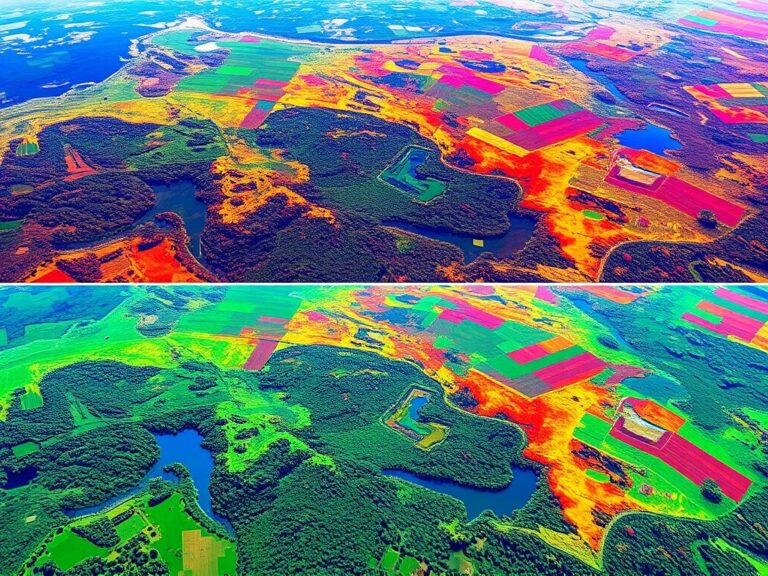
Vegetation indices, like the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), use math to analyze plant light reflection. They look at how plants reflect visible and near-infrared light. This helps spot and measure plant health and presence.
NDVI is great for finding and outlining urban green spots. This includes parks, gardens, street trees, and urban forests.
Classification Methods
Image classification sorts out different land types in cities. It uses smart algorithms to tell plants from non-plants and to spot certain plant types. This info is crucial for city planners and ecologists.
It helps them see where green spaces are and what they’re made of. This knowledge guides urban planning and green space care.
Change Detection Techniques
Remote sensing lets us watch urban plants over time. It uses old and new images to see how plants have changed. This could be more green spaces, lost trees, or urban growth.
This info helps shape green policies and plans. It’s essential for making cities greener and better.
These remote sensing tools are a powerful way to study and manage urban plants. They help experts and leaders make smart choices for our cities.
Advantages of Remote Sensing for Urban Vegetation
Remote sensing is a game-changer for managing urban greenery. It covers big areas, gives real-time data, and is affordable. This makes it a top choice for urban ecologists and planners.
Enhanced Coverage and Scale
Remote sensing beats traditional surveys by mapping entire cities easily. Satellites and planes capture detailed images of urban areas. This helps understand where and how green spaces are doing.
Real-time Monitoring
Remote sensing keeps urban greenery in check with up-to-date info. Satellites and planes fly over cities often. This lets us spot changes quickly, like trees falling or green areas growing. It’s key for making smart decisions and planning cities well.
Cost-Effectiveness
Remote sensing is cheaper than old-school field surveys. The initial cost is high, but ongoing costs are much lower. This is great for cities with tight budgets wanting to manage their green spaces better.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Coverage and Scale | Ability to map vegetation across entire cities, rather than limited ground-based surveys |
| Real-time Monitoring | Frequent satellite or aerial data capture enables timely detection of changes in urban vegetation |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower ongoing costs compared to labor-intensive field surveys for urban vegetation monitoring |
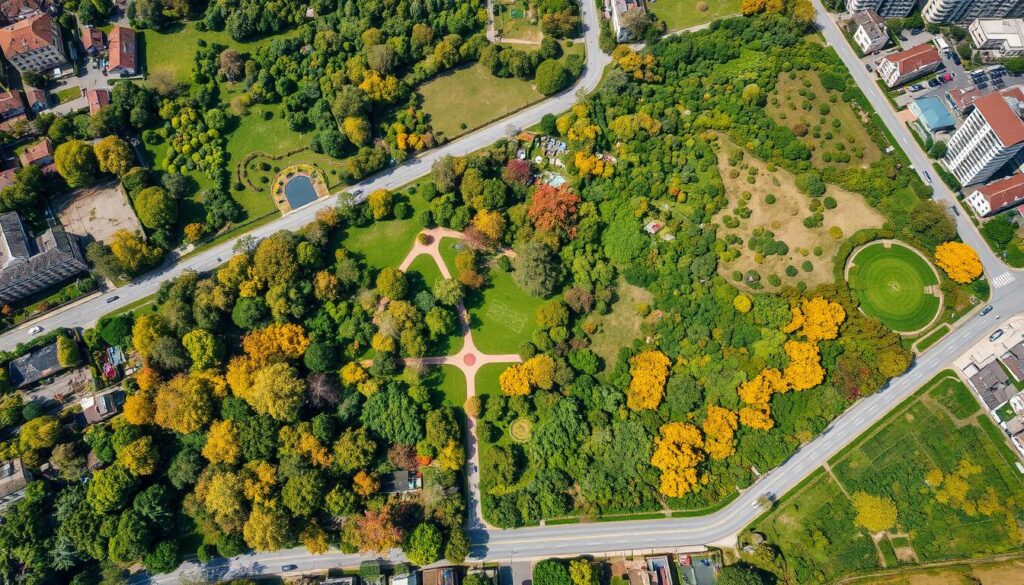

“Remote sensing has revolutionized the way we approach urban vegetation management, providing a comprehensive and cost-effective solution for cities seeking to enhance their green spaces and improve environmental resilience.”
Challenges in Remote Sensing
Remote sensing has changed how we map urban vegetation. But, it faces many challenges. It’s key to tackle these to get accurate data for better urban planning and environmental care.
Data Accuracy and Resolution
Data quality and detail are big concerns in remote sensing. Weather, clouds, and sensor limits can mess with the data. This makes it hard to spot and measure urban plants, especially in complex areas.
Interpretation Complexity
Figuring out remote sensing data for urban plants is tricky. Telling apart different plants and their health is hard in busy cities. Adding ground data and past records helps make the images clearer.
Environmental Factors Affecting Data
Weather, seasons, and city growth can change plant data. This makes it tough to track plant changes over time. Finding ways to handle these changes is key for good urban plant mapping.
| Challenge | Description | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Data Accuracy and Resolution | Limitations in satellite and aerial imagery quality due to factors like cloud cover and sensor limitations | Utilize higher-resolution sensors, combine multiple data sources, and apply advanced image processing techniques |
| Interpretation Complexity | Difficulty in distinguishing vegetation types and conditions in dense urban environments | Integrate ground-based data, employ machine learning algorithms, and develop specialized vegetation indices |
| Environmental Factors Affecting Data | Changes in weather, seasons, and urban development can impact vegetation spectral signatures over time | Implement temporal analysis, leverage historical data, and develop adaptive algorithms to account for environmental influences |
By tackling these issues, we can make the most of remote sensing for urban plant mapping. This helps make cities greener and better for everyone.
Case Studies of Urban Vegetation Mapping
Remote sensing has changed how we study and manage urban green spaces. It allows us to map and analyze city parks and gardens worldwide. Let’s look at three examples that show how powerful this technology is.
New York City
New York City, very crowded, uses remote sensing to understand its green areas. By looking at satellite images and aerial photos, experts can map trees, parks, and green spaces accurately. This helps the city plan better, keeping and growing its green spaces.
Los Angeles
Los Angeles, known for its big city feel, has a surprising story. Studies show the city’s green efforts, like planting trees and adding parks, have grown its green areas a lot. This data helps the city plan for a greener future and fight climate change.
Singapore
Singapore, called the “City in a Garden,” leads in urban green mapping. It uses satellite images, aerial photos, and LiDAR data to map its urban forest. This helps the city protect and grow its green areas, making it a model for other cities.
| City | Key Findings | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| New York City | Detailed mapping of tree canopy and green spaces | Inform urban planning decisions, preserve and expand green infrastructure |
| Los Angeles | Significant increase in vegetation cover over the past decade | Guide sustainable urban development and climate change mitigation strategies |
| Singapore | Comprehensive inventory of urban forest, identification of areas for conservation and expansion | Maintain Singapore’s reputation as one of the greenest cities in the world |
These urban vegetation case studies show how remote sensing helps us understand and manage city green spaces. This technology helps urban planners and policymakers make better decisions. It ensures our cities are sustainable and resilient for the future.
Applications of Remote Sensing in Urban Planning
Remote sensing technologies are changing urban planning. They help city officials and planners solve many problems. These include managing green spaces and fighting urban heat islands.
Green Space Management
Remote sensing is key for managing green spaces. It uses satellite images and aerial photos. This lets planners track changes in urban plants over time.
This data helps in planning green areas. It ensures cities have enough parks and green spaces. This helps fight the bad effects of city life.
Urban Heat Island Effect Assessment
Remote sensing helps with the urban heat island problem. This is when cities get much hotter than the countryside. It uses thermal data from satellites to find hot spots in cities.
Planners use this info to cool cities down. They promote green spaces and use cool roofs. This helps lower city temperatures.
Biodiversity Conservation
Remote sensing also helps with urban biodiversity. It maps urban ecosystems to find important habitats. This helps protect and improve urban wildlife.
By using remote sensing, urban planning has changed. It gives planners new insights into cities. This helps make cities better, greener, and more livable.
Future Trends in Remote Sensing for Urban Vegetation
Remote sensing is changing fast, bringing new ways to map and study urban plants. We’re seeing more use of artificial intelligence, better data sharing, and new sensor tech. These changes will greatly improve how we watch over urban green spaces.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI is set to change how we map urban plants. New algorithms will help spot and track plants more accurately. This means we can make better plans for cities and save time and money.
Increased Data Accessibility
More open data, like satellite images, will help everyone see urban plants better. This makes it easier for experts and the public to work together. It also helps communities get involved in making cities greener.
Advancements in Sensor Technology
New sensors will give us better info on urban plants. They’ll tell us more about plant health and what’s growing where. This info will help us manage urban green spaces better. Plus, drones and IoT sensors will let us monitor plants in real-time.
These changes in AI, data, and sensors are exciting for the future of urban plant mapping. They’ll help cities become greener, healthier, and more livable. Urban planners will have the tools they need to make cities better for everyone.
Policy Implications of Remote Sensing Data
Remote sensing data is changing how cities plan and manage their spaces. It helps with making cities more sustainable, fighting climate change, and getting people involved in local projects.
Urban Sustainability Goals
Remote sensing data is key for cities to meet their sustainability goals. It shows where and how well green spaces are doing. This helps planners and policymakers make better plans for parks and forests.
They can use this data to keep and grow green areas. This makes cities better places to live and work.
Climate Change Mitigation
Remote sensing data is also vital for fighting climate change. It helps map out how much carbon cities can absorb. This info guides decisions on planting more trees and creating green spaces.
These efforts help cities reduce their carbon footprint. It’s a big step towards a greener future.
Community Engagement Strategies
Remote sensing data helps get people involved in taking care of their neighborhoods. It gives detailed info on local green areas. This info helps residents take pride in their community.
Policymakers can use it for projects that involve the community. This includes education and community-led green initiatives. It builds a sense of ownership and responsibility.
Remote sensing data is a game-changer for cities. It helps make decisions that benefit everyone. With it, cities can become greener, stronger, and better places to live.
Conclusion and Future Directions
Remote sensing technology has changed how we study and manage urban green spaces. This article showed how it helps us understand and care for cities better. It gives us detailed, up-to-date information for making cities greener and more sustainable.
Recap of Key Insights
Remote sensing brings many advantages for studying urban plants, like better coverage and saving money. It also lets us keep an eye on things over time. We talked about different ways to map urban plants, from satellites to advanced Lidar tech.
We also looked at the challenges of using remote sensing. It’s important to keep the data accurate and consider how the environment might affect it.
Recommendations for Stakeholders
Looking ahead, remote sensing will keep being key for making cities better. Urban planners, policymakers, and leaders should use this tech to make smarter choices. It helps manage parks, fight climate change, and make cities better for everyone.
By using remote sensing with AI and making data easier to get, we can come up with new ways to help cities. Working together, we can make sure everyone benefits from using remote sensing to map urban plants.