AI for Geospatial Data Smoothing – Noise Reduction
AI for Geospatial Data Smoothing: Reducing Noise and Unveiling Insights
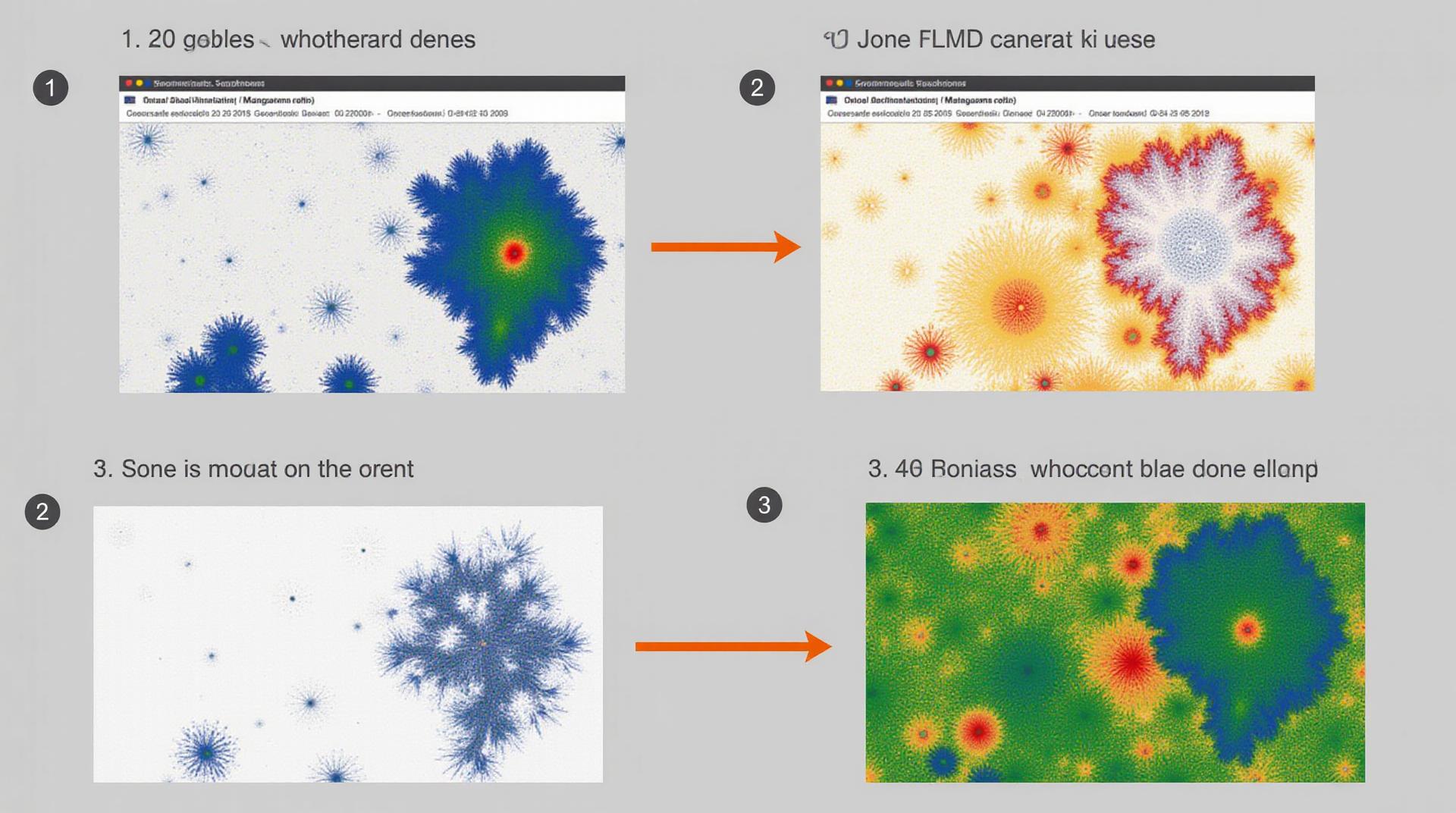
Unlocking the full potential of geo-intelligence hinges on the quality of your data. Geospatial data, encompassing imagery, sensor readings, and geographic information, often suffers from noise – unwanted artifacts like pixelation, clouds, shadows, and distortions. This stands as a significant hurdle for accurate analysis and informed decision-making. Enter AI for Geospatial Data Smoothing – a powerful approach to remove this noise, unveiling the underlying patterns and insights lurking within.
The Problem with Data Noise
Consider analyzing a wildfire’s spread. Distortions in imagery from sensors could hinder your ability to track the blaze’s trajectory and predict its potential impact on surrounding communities. Similarly, distorted data from satellite imagery could compound challenges when mapping agricultural yields. These scenarios showcase how even minor noise can negatively impact geospatial analysis.
Introducing AI for Geospatial Data Smoothing:
Artificial Intelligence provides an innovative solution to this ubiquitous issue. AI algorithms, trained on vast datasets of ‘clean’ geo-data, can filter out noise effectively, allowing for more accurate and insightful analysis. Think of it as teaching your AI assistant to recognize and remove unwanted noise so it can focus on valuing data content.
Key Features of AI in Geospatial Data Smoothing:
- Multi-Spectral Analysis: AI can filter out noisy pixels and sharpen imagery using multi-spectral analysis, revealing finer details and identifying subtle changes in the earth’s surface.
- Data Interpolation: AI algorithms can predict values between known data points, effectively filling in gaps and smoothing out transitions.
- Object-Based Analysis: AI can identify and categorize objects in geospatial datasets, enabling precise classification and tracking of weather patterns, infrastructure, and urban sprawl
- Deep Learning: Deep learning neural networks excel at identifying intricate patterns within noisy data, enabling highly sophisticated analysis to address complex problems.
Benefits of Utilizing AI for Geospatial Data Smoothing:
Here’s a glimpse of the valuable insights offered by AI-powered noise reduction:
- Enhanced Accuracy: By minimizing noise, AI improves the accuracy of geospatial datasets, leading to more reliable and informed decisions
- Automated Processes: AI removes the labor-intensive manual filtering that often comes with traditional data cleaning processes, streamlining workflows and increasing efficiency
- New Insights: Smoother data opens doors to previously uncharted scientific and social phenomena. For example, AI can analyze low-resolution imagery to discover hidden patterns in urban development.
- Sustainable Practices: AI-enhanced geospatial data management translates to more sustainable practices, by providing precise insights for resource planning and environmental monitoring.
Applications of AI in Geospatial Data Smoothing:
The applications of AI in geospatial data smoothing are diverse and impactful:
- Climate Change Monitoring: AI can accurately detect and analyze environmental events like wildfires, floods, and droughts through clearer imagery across vast landscapes.
- Disaster Risk Assessment: By analyzing satellite imagery after an event, AI can provide valuable insights into areas prone to damage and plan for efficient recovery.
- Precision Agriculture : AI assisted image smoothing helps farmers achieve greater yield thanks to accurate crop mapping, infestation detection, and targeted application of resources
- Urban Planning and Design: AI can analyze high-resolution aerial images to identify potential areas for development, optimize traffic flow, and promote efficient land use.
Resources for Exploring AI for Geospatial Data Smoothing:
Ready to delve deeper into this exciting field?
- Research Papers:
A-I for Geo-Spacial Data Smoothing - Online Courses:
Computer Vision - Cloud Integrations:
Wavelength
Become an AI Leader: Navigate Your Weg to a Smarter Geo-Intelligence Landscape
AI for geospatial data smoothing holds immense promise and presents exciting opportunities for individuals and organizations to rethink their approaches to data insights. From researchers exploring intricate ecological patterns to urban planners striving for efficient city management, AI-driven smoothness is set to be a cornerstone of impactful geospatial data analysis in the years to come.
Check similar topics:
GeoAI Noise Reduction FAQs
Get answers to frequently asked questions about geoAI noise reduction!
What is GeoAI Noise Reduction?
GeoAI noise reduction is a technology that uses AI algorithms to remove unwanted distortions and inconsistencies from geographic data. This allows for more accurate analysis and decision-making in various applications, from urban planning and mapping to environmental monitoring.
What Formats Does GeoAI Noise Reduction Support?
- Point data (latitude and longitude)
- Line data (usually in a shapefile format)
- Raster data (such as satellite imagery, aerial photographs)
Is GeoAI Noise Reduction Available for Public Use?
Yes! GeoAI noise reduction is available through our cloud-based API and is compatible with various programming languages.
How Do I Use GeoAI Noise Reduction?
You can easily integrate our API into your existing workflows or applications.
We provide comprehensive documentation and support to get you started.
How Can GeoAI Noise Reduction Improve My Applications?
- Improve accuracy of mapping and spatial analysis
- Enhance visual details in images and satellite data
- Eliminate noise for more effective analysis and visualization
- Enable smarter decision making in diverse fields
The Importance of GeoAI Noise Reduction
Continuing geopolitical complexity requires advanced data analysis to empower smarter decision making. GeoAI Noise Reduction plays a vital role in bridging information gaps and enhancing accuracy. It allows for a complete picture of Earth to reveal valuable patterns and insights that can be used to address urgent environmental problems, support efficient urban planning, and enable more effective disaster response.